Business Intelligence in Marketing
Focused marketing instead of gut feeling

For decades, marketing was done more or less on gut instinct. If more customers could be won or more products could be sold, a marketing campaign was considered successful. The fact that a lot of potential might be lost, that opportunities might not be used or that a marketing campaign might not work was known, but this could not be changed. In the meantime, things have changed: we simply and naturally collect customer data, data on our website visits, clicks on advertisements or opening rates of newsletters. But now the question arises whether we are already using this collected data optimally or whether more is possible in this regard. This is precisely where business intelligence systems come in.
What is Marketing Analytics?
Intelligent analyses can be used to optimise processes and activities in marketing. Here, customer data serves as the basis for predicting your behaviour and thus leads to cost savings and the avoidance of wastage due to targeted advertising Tailored customer approaches as well as efficient and effective marketing measures become possible through the analysis of available data and the precise identification of target groups. In addition, sales can be increased as marketing measures can be better adapted to customer needs through an increased understanding of the customers. In this way, customer satisfaction can also be raised.
>>Business intelligence in marketing helps you to address the right person at the right moment with the right marketing measure.<<
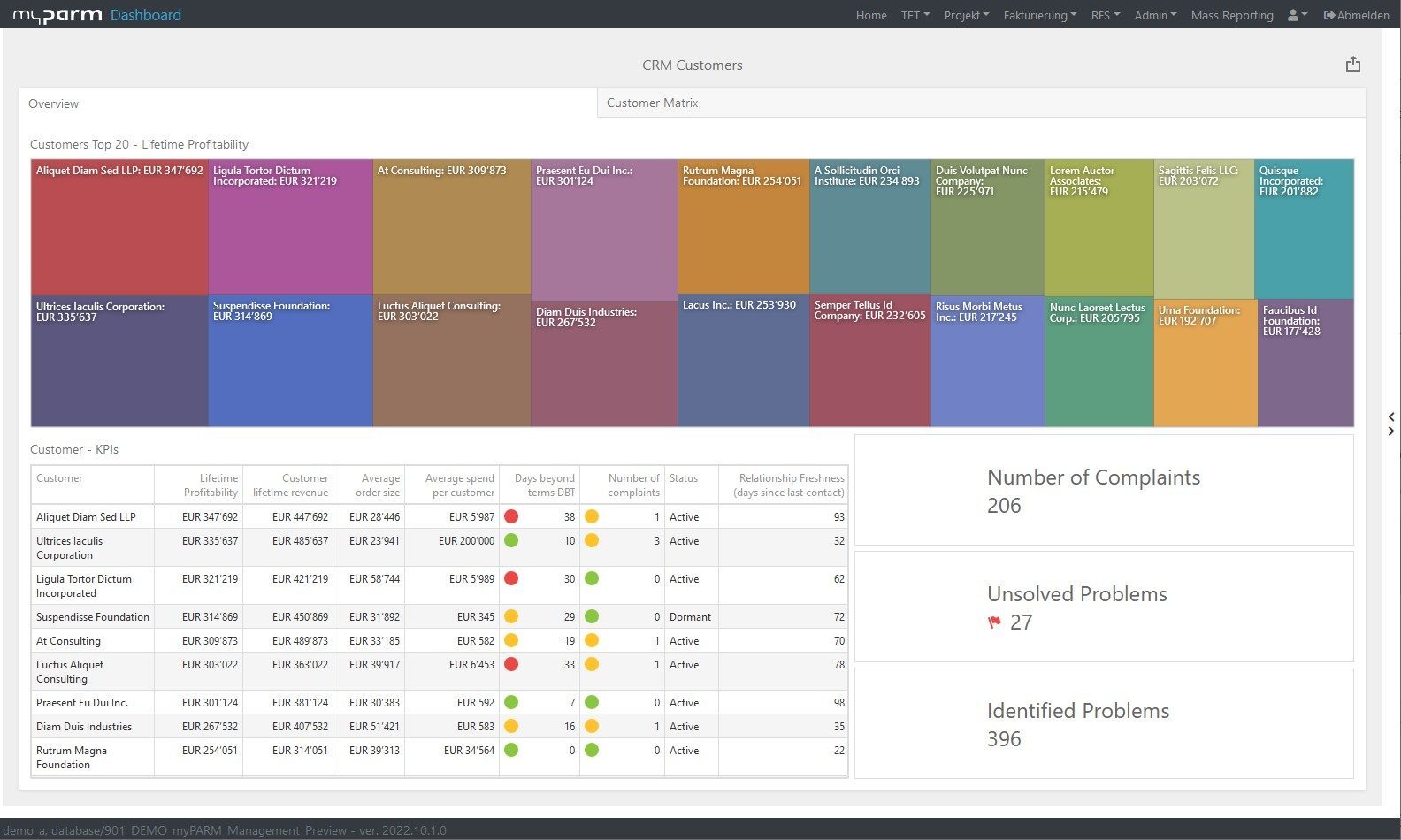
What customer data is collected?
Every interaction with you, regardless of the channel, generates customer data. This can be very different data: The email address given for the newsletter, the time someone spends on a product page or even a complaint. You can collect this data, in compliance with the General Data Protection Regulation (DSGVO). Some examples are:
- Customer master data or contact data: Name of person or company, address, email address, telephone number
- Purchasing behaviour: Turnover per purchase, number and type of products, payment methods, frequency of orders
- Budget
- Sales and sales potential
- Data from online tracking or product usage, e.g. which product pages were visited and how much time a customer spent on them, placements in the shopping basket of the online shop and whether these led to a purchase or not, the conversion rate, the route taken by a customer, clicks on advertisements, participation in events, how often someone returned to the website, etc
- Newsletter subscriptions, open rate, clicks on newsletter articles, unsubscriptions from the newsletter
- Complaints
What opportunities do marketing analytics offer?
- Fast and simple reports: Standardised reports from business intelligence tools enable up-to-date reports on all marketing actions at all times. On the one hand, you can save time when creating reports and on the other hand, you can easily check the effectiveness of your marketing measures. If you then recognise, for example, that a campaign is not working as it was intended, you can intervene quickly.
- Optimise customer experience: With marketing analytics, you get to know your customers, their needs and wishes better. From insights into the customer journey, i.e. the behaviour of customers across different channels, you can identify what needs a customer has and thus provide them with personalised offers. In this way, you can attract new customers as well as encourage existing customers to buy again and prevent them from leaving. In addition, you can improve the customer experience by recognising at which hurdles customers often drop out and why or what information they need at which point. Such patterns can also concern, for example, the typical behaviour before a cancellation or an order. If you recognise these patterns, you can derive measures from them to achieve the desired behaviour among customers. In addition, data analyses can help you to identify and analyse trends, such as when a specific product is only purchased in summer months. Once you have understood why such a trend exists, you can adapt your marketing measures to it. Marketing Intelligence can also support you in forecasting the sales of products.
Furthermore, you can divide your customers into segments according to demographic, geographic and psychographic aspects or even behaviour-oriented. This gives you the opportunity to design personalised marketing measures specifically for these segments. - Customer retention: With marketing analytics you can see which measures have retained a customer for a particularly long time or how a customer group reacts to certain campaigns. Furthermore, with the help of customer value predictions, high-yield customers can be distinguished from lower-yield customers. This helps, for example, when deciding whether investments in a customer relationship are worthwhile or not.
- Cost reduction: With tracking information, for example from websites, newsletters and social media, you can learn to understand how and when you should contact a customer. It also allows you to make personalised offers based on customer needs. In this way, you can optimally allocate your marketing budget to the different channels and avoid wastage.
- Pricing: Manufacturing Intelligence helps you to understand what your pricing strategy should look like from a production perspective. But this is only one side of the coin. With Marketing Analytics you can understand what the optimal price for your customers looks like, for example by analysing similar products to determine the product value for the customer. You can then adjust your pricing strategy accordingly.
- Ongoing marketing optimisation: Business Intelligence also helps you in the day-to-day business of marketing, as it provides you with clear analyses of important factors such as search engine optimisation, geomarketing or campaign success. In this way, you can see how effective a marketing measure is at any time and react flexibly as well as data-based to the results.
- Process optimisation: Internal marketing processes can also be analysed with Business Intelligence, so that optimisation potential can be identified here.
Conclusion
Using Business Intelligence in marketing can bring you many advantages, especially since extensive data is usually already collected in marketing. Optimal reports and flexible analyses enable you to quickly and easily assess the effectiveness of your marketing measures and react to customer needs. However, marketing intelligence also helps you to plan future measures, execute them in a targeted manner and determine the optimal budget for them.
Business Intelligence software that brings together data from a wide range of sources and makes it available for analysis helps you with cross-campaign analyses. In this way, you can control your marketing actions, get an up-to-date and simple overview of all relevant key figures at the push of a button and gain valuable insights.
Learn more about the Business Intelligence Software Software myPARM BIact:
Would you like to get to know myPARM BIact in a demo presentation? Then make an appointment with us right away!
