Project Management ABC: R for Resource Management
With optimal resource usage for a successful project

The captain of a ship sailing through unknown waters has a clear goal in mind that he wants to achieve. However, he has only limited resources available on his ship: this applies to the number of sailors and their skills as well as to supplies of food or water. To ensure that the goal can be achieved with the limited available resources, he needs effective resource management. Similarly, when implementing projects, a project manager has only limited resources available, such as employees, budget, time, or materials, to lead the project to success. We explain how you can set the sails of your projects on a course for success thanks to good resource management.
What is Resource Management?
Resource management is an important component of any project. It refers to the effective use of available resources to achieve a project’s goals. Resources can be anything needed for the project, including finances, employees, skills, materials, and time. The goal of resource management is to ensure that all available resources are used optimally to complete the project within budget and schedule.
To carry out effective resource management, project managers must have a clear idea of which resources are needed for the project and to what extent they are needed. A thorough needs analysis can further help to determine which resources should be prioritized and how they should be allocated. Additionally, project managers must understand exactly which resources are available to them at any given time. Only then can the optimal resources be assigned to the tasks and activities of a project. During the implementation of a project, monitoring and control of resource usage is also necessary to optimize its use or to adjust it if necessary.
The Types of Resources
Various types of resources are needed in projects, and each project can have different resource requirements. Some of the most common types of resources needed in projects are:
- Financial resources: Financial resources are one of the most important resources in any project. They include the budget available for the project, as well as the costs for materials, equipment, services, and personnel. For the project to stay within the financial constraints, project managers must ensure that the available budget is used effectively.
- Human resources: Human resources include all individuals involved in the project, including the project team, contractors, as well as external experts. To complete a project, project managers must deploy the right personnel with all the necessary skills and experiences. However, the necessary personnel are usually not exclusively available for work on a project but also have other tasks or responsibilities. This must be considered in resource management so that personnel are used effectively. Special cases such as vacations or work absences due to illness must also be planned for in resource management to successfully complete projects.
- Material resources: Material resources include all physical materials needed for the project, including equipment, tools, and raw materials. To meet the requirements of a project, project managers must ensure that the right material is available in sufficient quantity and quality.
- Time resources: Time is a scarce resource in almost every project. Therefore, good time planning is also part of resource management. Project managers must ensure that enough time is allocated for each task and activity of the project and that the progress of the project is regularly monitored to complete a project within the set time frame.
- Information resources: Information resources include all information needed for the project, including reports, databases, research results, or expert knowledge. Project managers must ensure that they have access to the necessary information to meet the requirements of the project.
Techniques in Resource Management
Although there are various types of resources, managing employees is often the most complex, as more factors need to be considered than other types of resources. Skills, availability, cost, and, in some cases, a location must be considered. Resource management should, therefore, answer the following questions:
- What resources and skills are needed for a project?
- Which resources are available at which times?
- What skills do existing employees possess, and are additional skills required to successfully implement a project?
- Where are existing resources currently used and where will they be used in the future?
- What capacities are available, taking into account resource failures or other tasks of employees?
Therefore, several resource management techniques can be used to create transparency and make the right decisions.
- Resource allocation: This technique refers to the allocation of resources to specific tasks or activities within the project and helps to ensure that each activity is performed with the right resources as well as that available resources are optimally utilized. Both the skills that each team member brings, and their availability as well as capacity are considered. Allocation reports help identify which skills and capacities are currently available or will be in the future. This way, you can plan for optimal use of resources for your project.
- Resource utilization: To achieve the most optimal use of your resources, your team’s capacities should be transparent. This way, you can ensure that available resources are not overloaded or underutilized. A utilization report can show how your team spends its time through charts and tables. This way, you can identify whether it is possible to improve efficiency, productivity, or performance while keeping the workload within reasonable limits.
- Resource matching: Resource matching is used to coordinate resources so that they are optimally used, and there are no conflicts or bottlenecks. The supply and demand of resources should be balanced before hiring additional employees or external service providers. To do this, you should know all the skills of your employees and find out if any gaps can be closed to minimize resource requirements. Resource matching can be supported by planning buffer times and setting priorities for resource provision.
- Resource forecasting: Resource management not only helps to ensure that ongoing projects can be carried out smoothly, but also enables proactive planning of resource needs and availability for future projects. If current capacities and future projects are known, resource forecasting can help to identify bottlenecks at an early stage and take action to ensure that the required resources are available when they are needed. Such resource forecasting can be done, for example, using historical data and assumptions about future trends.
- Resource pooling: By creating a resource pool, resources can be better utilized across different projects, and synergies can be created.
- Resource splitting: Resource splitting can help optimize resource utilization and avoid bottlenecks by using individual resources among several tasks or activities within a project.
- Resource procurement: If there are not enough internal resources available, resource acquisition is used to obtain the necessary resources from external providers. This can help overcome bottlenecks and ensure that a project has the required resources available.
- Resource optimization: During the implementation of a project, changes often arise. Resource optimization is intended to ensure that the available resources are still used effectively. This can reduce the waste of resources while increasing the efficiency of resource utilization.
The phases of resource management
Resource management generally goes through three phases:
1. Resource planning:
When a project is planned and its objectives, as well as scope, is known, this phase identifies the necessary resources and develops a strategy to ensure that the required resources are available at the right time. This includes creating a resource management plan. The following steps are necessary for the planning phase:
- Identification of required resources: First, all the resources needed for the project must be identified.
- Analysis of resource availability: Then, you should determine which resources are available internally and which ones need to be acquired externally.
- Prioritization of resources: You should also clarify, which resources are needed to what extent and what priority they have.
- Development of a resource management plan: This plan determines how resources will be acquired and assigned, and alternative plans are developed to respond to unforeseen events or bottlenecks.
Techniques used in this phase to estimate the effort include bottom-up estimation, top-down estimation, expert estimation, analogy estimation, and the Delphi method, all of which help to estimate the required resources as accurately as possible.
2. Resource acquisition and assignment:
In the next phase, the required resources are acquired and assigned to the various tasks or activities of the project. It is ensured that the resources are used effectively, and bottlenecks are avoided. The following steps are included:
- Resource acquisition: First, you need to decide which resources can be obtained internally and which ones need to be obtained externally. Offers have to be compared and contracts should be negotiated.
- Resource assignment: Based on this, you can decide which resources are assigned to which tasks and activities, as well as when and for how long they are needed.
- Consideration of bottlenecks: It is important to ensure that bottlenecks are avoided by assigning resources in such a way that they are used as effectively as possible.
To optimize the allocation of resources, techniques such as network planning, Gantt charts, the critical path, or the resource leveling model are often used in this phase.

3. Monitoring and Control of Resources:
During the implementation of a project, continuous monitoring and control of resources are carried out to ensure that resources are being utilized correctly and that the project remains within the specified time and cost constraints even in the event of unforeseen changes. Various reports and analyses aid in this process:
- Status reports: Status reports are regular reports on the progress of the project as well as the use of resources. They help the project manager to monitor progress in terms of resource utilization and to detect issues in an early stage.
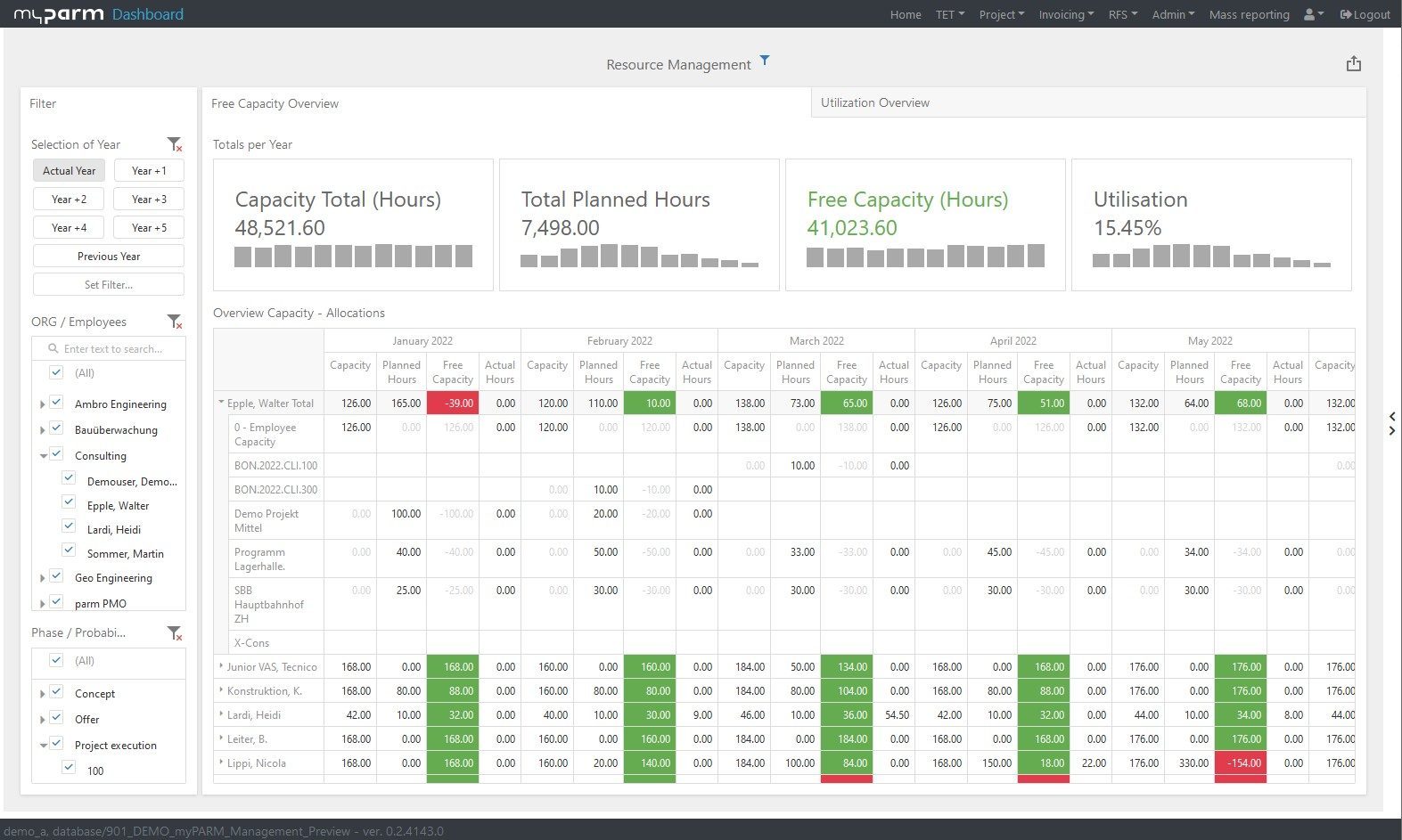
- Work hours: Tracking work hours is an important part of monitoring and controlling human resources. Actual work hours are compared to planned work hours to determine if the project is on schedule and if resources are being utilized effectively.
- Earned Value Analysis: Earned Value Analysis is a method used to measure the progress of a project by comparing the value of the work completed to the planned value. This allows the project manager to determine if the project is on schedule and within budget.
In addition, effective risk management should be carried out, to identify and evaluate potential risks and to ensure that possible resource constraints can be avoided. A good change management process also helps to manage and communicate necessary changes to the project plan or resource utilization.
Resource Management in Project Portfolio Management and PMO
In Project Portfolio Management (PPM), resource management is particularly important as a variety of projects within a portfolio need to be effectively managed and the optimal utilization of a company’s limited resources needs to be ensured. Compared to a single project, distributing resources across multiple projects in PPM presents a greater challenge.
Therefore, for resource management in PPM, all available resources needed for the project portfolio should be evaluated first, including external resources such as consultants or contractors. Next, the possible projects in the portfolio should be prioritized based on their strategic alignment, their benefit to the company, as well as their resource requirements, so that the available resources can be optimally distributed across projects. This requires careful coordination to ensure that all projects receive sufficient resources. During project implementation, resource monitoring and control must be carried out also in PPM to ensure that resources are being used effectively. This includes tracking resource utilization, identifying bottlenecks, and implementing measures to optimize resource utilization.
In a Project Management Office (PMO), resource management is typically performed by specialized resource managers who are responsible for planning, assigning, and monitoring resources within the portfolio. The PMO works closely with project managers to ensure that resources are used effectively and efficiently, and to ensure that all projects within the portfolio are completed.
Resource Management in Agile Projects
In agile projects, there are some differences in resource management compared to traditional project management. For example, resource management in agile projects is more flexible and dynamic than in traditional project management. Agile teams can quickly react to changes and ensure that the right resources are available at the right time to complete the project. Some of the key aspects of resource management in agile projects are:
- Self-organized teams: Agile teams often have more autonomy than traditional project teams and can determine their own resource needs. They can make their own decisions about which resources are needed and how they should be used.
- Agile planning: Agile planning is based on the idea that plans and requirements can change throughout the project. Therefore, resource management in agile projects is often more flexible so that it can be quickly adapted to changes.
- Iterative development: Agile projects rely on iterative development, which means that the team works in short sprints and receives regular feedback. This iterative development allows the team to quickly react to changes in resource needs.
Benefits of Resource Management in Projects
- Effective use of resources: Effective resource planning and allocation can optimize the use of resources to achieve project goals. This reduces the waste of resources and helps to lower project costs. At the same time, good resource management also helps to prevent resource overload.
- Better predictability: Accurate resource planning allows project managers to better plan project progress and manage processes more effectively. The risk of delays and bottlenecks is minimized, so that the project can be completed on time and within budget.
- Optimal overview: Good resource management helps to facilitate informed decision-making by providing a clear view of resource availability and utilization. This helps in selecting options or alternatives and contributes to the successful implementation of the project.
- Effective communication: Resource planning and allocation also help in effective communication with all project stakeholders. This includes conveying information about resource needs and availability, as well as possible risks and challenges.
Challenges of resource management in projects:
- Additional effort: Resource management requires additional effort and can take up a lot of time in implementing a project. This can be perceived as excessive, especially in smaller projects.
- Complexity: Resource management can be very complex and often requires precise coordination among various project stakeholders. This can lead to additional challenges and difficulties that make project implementation more difficult.
- High demands on project managers: Effective resource planning and allocation require close collaboration and coordination between the project manager and other project stakeholders. The project manager must have in-depth knowledge and experience in resource management and should be able to effectively control resource utilization.
- Risk of errors: Errors in resource planning and allocation can lead to delays, bottlenecks, and cost overruns. Accurate monitoring and control of resource utilization are therefore essential to minimize these risks.
Tips and tricks
- Define clear project objectives: It is important to define clear project objectives and ensure that all project stakeholders understand them. This helps to effectively plan and manage the required resources.
- Create a detailed resource plan: A detailed resource plan can help ensure that all required resources are available exactly when they are needed. The plan should include all necessary resources, their costs and availability, as well as the timeframe for their use.
- Manage resources centrally: A central management of resources, for example in a resource pool, helps to effectively use resources across numerous projects and avoid bottlenecks.
- Monitor resource utilization: It is important to regularly monitor the utilization of resources to ensure that they are being used optimally. This can help to identify overloads or underutilization early on and to respond accordingly.
- Ensure all resources are up to date: It is important to ensure that all resources are up to date and meet the requirements of the project. This helps to ensure the quality of the project and minimize potential risks. In addition, thanks to proactive planning, you are always prepared for future projects.
- Keep an eye on costs: Effective resource management always requires monitoring costs. Make sure that resource costs stay within budget and that costs are appropriately adjusted as the project progresses, if necessary.
- Maintain communication: It is important to maintain communication with all project stakeholders to ensure that everyone is informed about the status of resource planning and management. Regular communication can help to identify bottlenecks or issues early on and resolve them quickly.
- Learn from past projects: Use past projects as a learning opportunity to see what worked well and what did not. Use this knowledge to optimize resource usage in future projects.
- Be flexible: Plan for a certain degree of flexibility in your resource planning to account for unforeseen events or changes in the project timeline. This helps to respond quickly and effectively to changes.
- Continuous improvement: Resource management should be viewed as a continuous improvement process. This allows it to be continually optimized.
Conclusion
Resource management is a crucial success factor for projects. Careful planning, allocating, monitoring, and controlling of resources help to complete projects, optimize the use of available resources, as well as optimize time, cost, and quality.
Especially for large projects or entire project portfolios, it can be difficult to overview the available and required resources. Therefore, suitable project management software such as myPARM significantly facilitates the planning, allocation, and monitoring of resources. With myPARM, resource needs and availability can be effectively tracked at the project and portfolio level. The software also offers comprehensive dashboards and reports that enable accurate evaluation of resource usage.
Learn more about the project and portfolio management software myPARM:
Would you like to get to know myPARM in a demo presentation? Then make an appointment with us right away!
