The BCG Matrix in Project Management
Successful thanks to the right prioritization of your projects

The 60s – a time of social change and upheaval, where hippies dreamed of “love and peace,” astronauts set foot on the moon for the first time, and the Beatles as well as rock ‘n’ roll dominated the charts. But it was also a time when the Boston Consulting Group developed an innovative idea for managing companies that remains a crucial tool up to this day. While many former hippies now enjoy their well-deserved retirement, the BCG matrix is still used to evaluate products and projects as well as to optimize resource utilization.
What is the BCG Matrix?
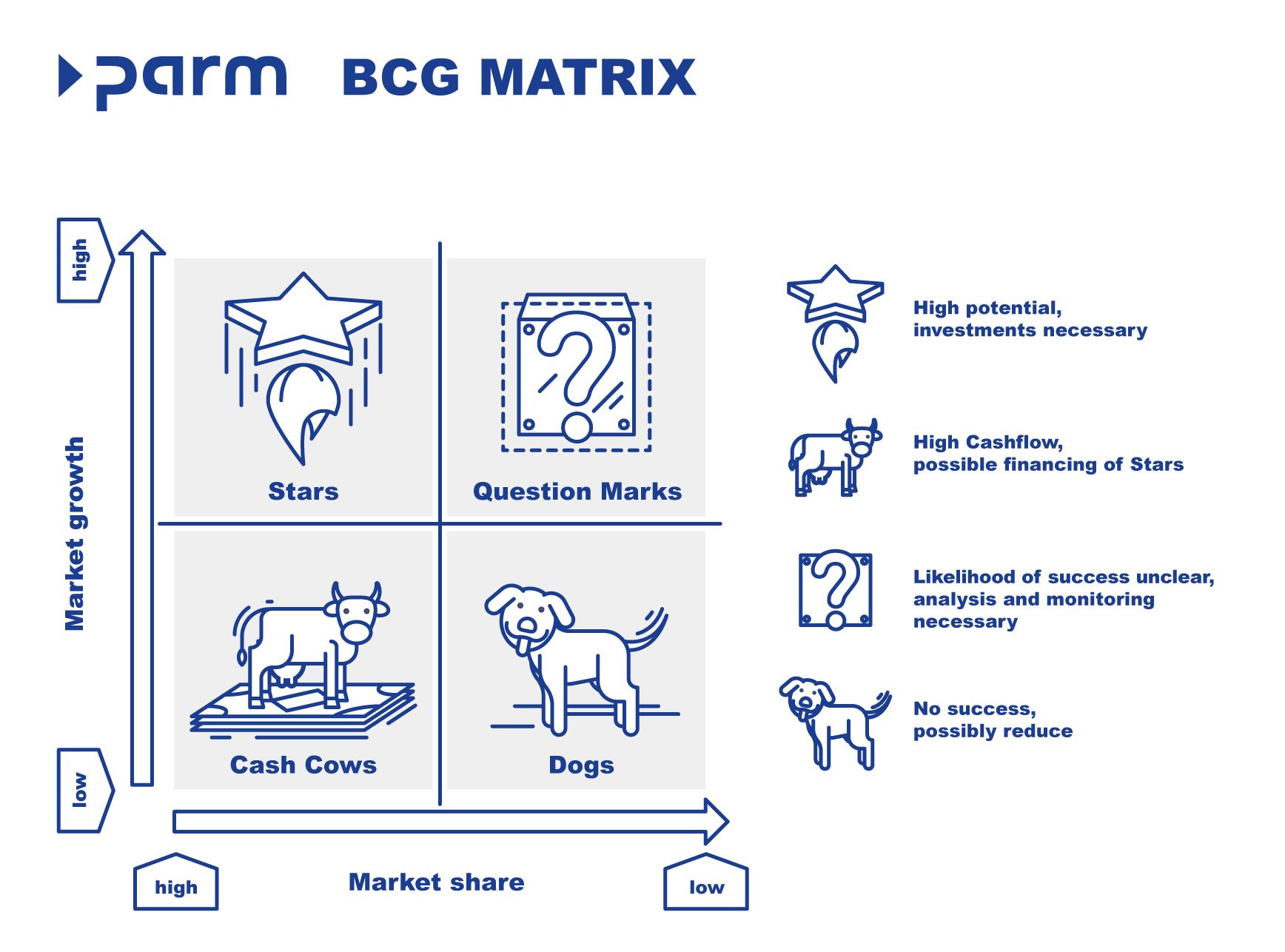
The BCG Matrix is a concept in strategic corporate planning, also known as portfolio analysis. It was developed by the Boston Consulting Group in the 1960s as a useful tool for prioritizing business units and projects based on market growth and market share. The business units under examination are categorized into four groups: Stars, Cash Cows, Question Marks, and Dogs. Strategic decisions are then made based on this categorization. Therefore, the matrix is an essential part of strategic planning and helps companies effectively allocate their resources to maximize their growth potential.
How does the BCG Matrix work?
The BCG Matrix is typically applied in five steps:
1. Identification of business units
The first phase involves identifying all business units within a company. These can be products, services, brands, business fields, or even projects.
2. Market share analysis
The next step is to determine the market share of each business unit. This can be done, for example, by conducting market research to gather information about the market, customers, and competitors. You can also conduct surveys, analyse focus groups, gather expert opinions, or examine industry reports from research and consulting firms. A competitor analysis can help evaluate your company compared to the competition. Additionally, your own sales figures can serve as an indicator of market share as well as the market growth to be analysed in the next step. Therefore, you can utilize data such as revenue, profit, or sales volume to estimate your market share.
3. Market growth analysis
The third step involves evaluating the growth potential of each business unit. You should therefore conduct an analysis of market trends, market potential, and competition. Again, you can use market research, expert opinions, or competitor analyses for this purpose.
4. Placement of business units in the matrix
In the next phase, business units are categorized into the four quadrants of the BCG Matrix based on their market share and market growth.
- Stars have a high market share in a rapidly growing market. These business units have high growth potential but often require significant investments to fully exploit this potential.
- Cash Cows have a high market share in a mature market. These business units are stable and typically generate high profits. They require only limited investments to maintain their market position but exhibit no or only low market growth.
- Question Marks have a low market share in a rapidly growing market. Thus, they have high growth potential but also carry high risks, as it is unclear whether they will be successful or not. They often require significant investments to capitalize on their potential.
- Dogs have a low market share in a mature market with no significant growth potential.
5. Setting priorities and defining strategies
After categorizing the business units, you can create a priority list and establish strategies for each quadrant or business unit.
- Stars have the highest growth potential and are likely to be profitable. They have already been successfully introduced to the market and have gained new market shares. Therefore, a possible strategy is to prioritize and invest in stars to fully exploit their growth potential. This may involve further developing a product or project, expanding capacities, or exploring new distribution channels.
- In contrast, Cash Cows can serve as a source of financing for other products or projects since they generate high cash flow but have limited growth potential. They are self-sustaining with a high demand or market share and may even be market leaders. The recommended strategy for business units in this category is to capitalize on the profits generated and invest those in Stars. To maximize profits and increase profitability, it is also possible to optimize these products or projects by improving production, reducing costs, or automating processes.
- Question Marks are projects or products for which the likelihood for success cannot yet be estimated. Usually, these are product innovations or new products positioned in growth markets with little or no market share. They should be carefully analysed to determine whether they can become Stars, where investments pay off and market shares are gained, or if there is a greater likelihood that they will fall short of expectations and become Dogs. By conducting a thorough analysis and closely monitoring them, you can better understand the question marks and decide on a strategy to prevent these projects or products from becoming a cost burden.
- Dogs have limited growth opportunities and generate little cash flow, meaning they have not met expectations and have not achieved desired sales. It is usually recommended to reduce products or projects in this area, by for example reducing production capacity, discontinuing them altogether, or reducing marketing budgets. However, with a thorough analysis, Dogs can also become profitable. For example, a relaunch with an improved product can be promising. It may also be the case that a market was not ready for a specific product at a certain time but would present good market opportunities later. Additionally, seasonal, inflationary, or political factors can hinder a product or project, so it may be wise to wait until the situation improves and demand increases.
When choosing the right strategy for a product or project, other factors should also be considered, such as company goals, available resources, or market conditions. Therefore, the BCG Matrix can only provide potential strategies that should be carefully evaluated afterwards.
Application of the BCG Matrix in Project Management
The classic BCG Matrix can also be applied in project portfolio management to evaluate and prioritize projects based on their prospects for success. However, the axes of the BCG Matrix can also be adjusted to perform a portfolio analysis based on additional criteria. Often, the axes of time / resources and impact are used.
- Time / resources: This axis indicates the amount of time and resources required for a project. Projects can be classified on this axis from low to high requirements.
- Impact: The impact axis indicates the importance of a project to the company. Projects can be categorized on this axis from low to high significance for the company.
The combination of these two axes results in the following four quadrants:
- Stars (high time / resource requirements, high impact): Projects in this quadrant are of high importance to the company but also require significant time and resources. These projects should be prioritized and strategically managed as they have the potential to increase the company’s growth and profitability.
- Cash Cows (low time / resource requirements, high impact): Projects in this quadrant have high significance for the company but require minimal time and resources only. These projects should also be prioritized as they hold high potential for the company, but they need to be carefully monitored to ensure they deliver the expected benefits.
- Question Marks (high time / resource requirements, low impact): Projects in this quadrant require a considerable amount of time and resources but have low significance for the company. These projects should generally be avoided or given low priority as they do not contribute significantly to the achievement of the company’s strategic objectives.
- Dogs (low time / resources requirements, low impact): Projects in this quadrant require minimal time and resources while also having low significance for the company. These projects can be given low priority or even halted altogether as they do not contribute significantly to the achievement of the company’s strategic objectives.
By conducting this portfolio analysis using the BCG Matrix, you can gain a clear overview of your project portfolio and prioritize projects effectively. This ensures that you allocate high priority to the right projects, optimize your resources, and achieve the strategic goals of your company. However, in project management or project portfolio management, there are further factors to be considered before making a final decision regarding project prioritization. Factors such as project budget, risk assessments, or customer needs, for example, must also be taken into account.
Advantages
- Focus on promising projects: The BCG Matrix helps companies concentrate their resources on the most profitable projects. This allows them to optimize their limited resources and increase the profitability of the company.
- Risk reduction: Additionally, the matrix helps to reduce risks by prioritizing projects that have the best ratio of potential success and resource investment.
- Achievement of strategic goals: The BCG Matrix can also support strategic planning by contrasting long-term goals with short-term priorities.
- Communication: Furthermore, the BCG Matrix provides a simple and visual way to communicate projects and their potential. By using the matrix, your project portfolios are presented in a clear and concise manner, making it easier to convey decisions regarding project prioritization.
Disadvantages
- Simplified representation: The BCG Matrix offers a highly simplified representation of the project portfolio and does not consider all factors necessary for a comprehensive evaluation of the projects. Other factors such as technology influence, competition, regulatory factors, environmental factors, or the business model can also impact the success of a project but are not included in the BCG Matrix.
- Time dependency: The evaluation of projects in the BCG Matrix is time-dependent. For example, a project classified as a Star at the time of analysis may no longer fall into that category shortly after. Therefore, companies need to continuously monitor their project portfolios and update the matrix to ensure that decisions are based on current data and trends.
- Flexibility: In project management, the BCG matrix may also be unsuitable when operating projects in a highly dynamic or uncertain market. In such cases, the BCG matrix may not consider all factors that influence the potential and profitability of a project, so a more comprehensive evaluation method may be required.
Adjustments to the BCG Matrix
To tailor the BCG matrix to specific needs and mitigate its disadvantages, it can be adjusted in the following ways:
- Axis modification: To consider specific factors relevant to a company or a particular industry, the axes can be adjusted as we showed in the case of project portfolio management. For example, factors like technological development or customer demand could be included.
- Use of KPIs: It is also possible to adapt the BCG matrix using key performance indicators (KPIs) relevant to the company or industry. Instead of revenue or market share, metrics such as profit margin or customer ratings can be used, providing clear and traceable data as the basis for the matrix.
- Segmentation: The BCG matrix can also be created individually for different segments to analyse specific business areas or markets separately. For instance, you can examine various regions or product categories.
- Combination with other tools: Combining the BCG matrix with other tools or methods also makes it possible to conduct a more comprehensive analysis. For example, the matrix can be combined with a SWOT analysis or a value chain analysis.
Conclusion
The BCG matrix is a useful method for evaluating projects and setting priorities in project portfolios, as it categorizes projects into different groups that require different strategies. This allows companies to efficiently utilize their resources, identify opportunities, and minimize risks.
However, it is important to understand the limitations of the BCG matrix and complement it with other evaluation methods or tools to conduct a more comprehensive analysis. In this regard, project management software like myPARM can be helpful as it not only integrates the results of the BCG analysis but also enables a comprehensive analysis of your project portfolio based on criteria defined by you. This way, you can make informed decisions based on a holistic view of your project portfolio and optimize it to achieve your company’s strategic goals.
Learn more about the project and portfolio management software myPARM:
Would you like to get to know myPARM in a demo presentation? Then make an appointment with us right away!
