This is how Business Intelligence helps with your corporate strategy
Aligning the focus of all employees with clear key figures

A corporate strategy is designed to set a company up for success. But even the most brilliant strategy is doomed to fail if your employees do not understand how their daily work contributes to achieving your goals. Therefore, to properly align your team’s focus, the strategy should be translated into clearly understandable and measurable metrics. Business intelligence can help you define the strategy, set the right metrics and check their status.
Use BI to develop your strategy
If you want to strengthen your competitive advantages with your strategy, you should first identify them. While many companies rely on gut feeling, you can also use facts to identify your strengths. If you combine market research results with historical data, for example, you can uncover trends and identify opportunities. This can help you come up with ideas for a new product, for example, or recognise that you should focus on a specific market. You can then set your business strategy accordingly.
Translate strategy into measurable goals
Once you have a strategy in place, the next challenge is to select the right metrics to measure its progress and break them down to individual departments or individual employees. Identifying the right metrics will determine what your business intelligence system will analyse and what it will show in dashboards. In this way, each employee should be able to see how he or she can contribute to achieving the defined goals. Therefore, you should determine which key figure should reach which target value. This target value should be challenging, but at the same time achievable, so that your employees are not demotivated by unrealistic or too low targets. To set an appropriate value, you can use historical data analysis and data forecasts from business intelligence tools.
How to find the right key figures
There are absolute key figures, such as profit, turnover or scrap, or relative key figures that relate two values to each other, such as productivity, where you put the result of a process in relation to the effort put into it. In addition, there are also qualitative indicators that are often used in connection with sustainability topics. However, not every possible indicator makes sense and is useful for your strategy. KPI (Key Performance Indicator) is the term used to describe the main key figures you track. It is true that you can consider all the figures that you determine in relation to your company as a key figure. Ideally, however, a few selected KPIs are sufficient to show the entire business processes at a glance.
These five to ten KPIs are determined in accordance with your corporate strategy. Here, the following points are important:
- Is the indicator assessable, i.e. can values be defined that are either good or poor?
- Does the indicator correspond to the corporate strategy? You can determine whether a key figure makes sense for you by answering a few questions:
- What result is desired?
- Why is it important in the context of the corporate strategy?
- How is progress measured?
- How can the result be influenced?
- Who is responsible for it?
- How is it determined whether the goal has been achieved and how is progress monitored?
Example turnover: An increased turnover alone says nothing about the actual business success. It may be that the turnover increases, but at the same time the costs increase so much that the profit is negative. Therefore, if the business success is to be measured, it makes more sense to relate the turnover and the costs to each other in order to determine the profit (turnover – costs = profit). Conversely, an increase in profit does not necessarily mean that turnover has also increased, as it could be that costs have simply decreased. So if your business strategy is geared towards market growth, profit is not a useful metric.
- Is the data required for this clean? If KPIs are calculated from incomplete or incorrect data, the result will also be wrong.
- Are the KPIs clearly understandable? Everyone who uses the KPIs should understand exactly how they are calculated and what they mean. This avoids ambiguities and room for interpretation.
- How can a key figure be influenced? In order for every employee to know how they can contribute to the company’s success, they should not only know the key figures, but also understand what they can do to influence them positively.
- What is done if the values do not develop as desired?
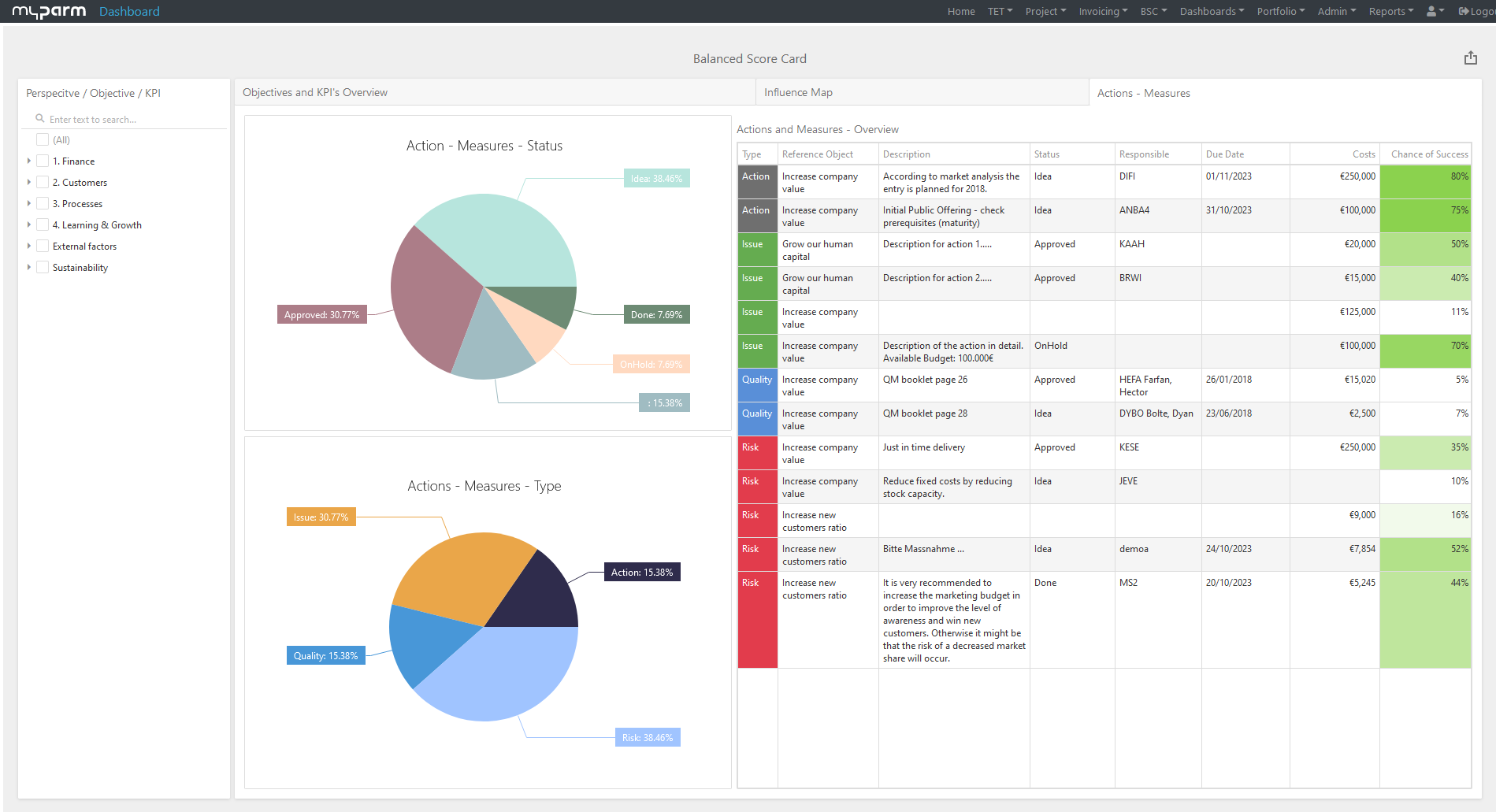
A Balanced Scorecard (BSC) makes your strategic goals and key figures visible in a simple way. This helps you to implement your corporate strategy and to check the current implementation status at any time.
Examples of key performance indicators
For each business area, there are countless KPIs you can track that represent the pursuit of your business strategy in different ways. Here is an overview of some of the most important KPIs in different business areas:
1. Financial key figures
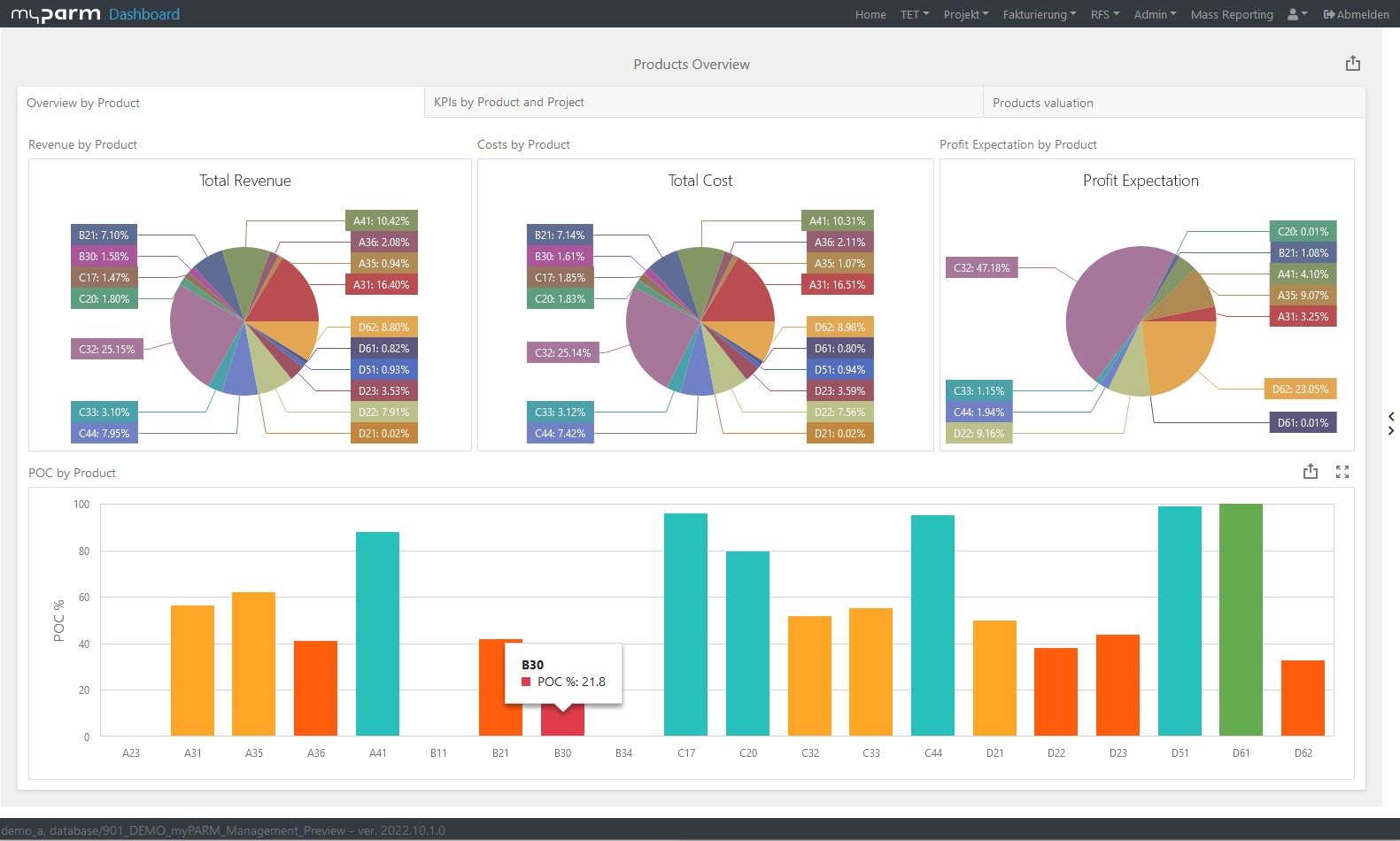
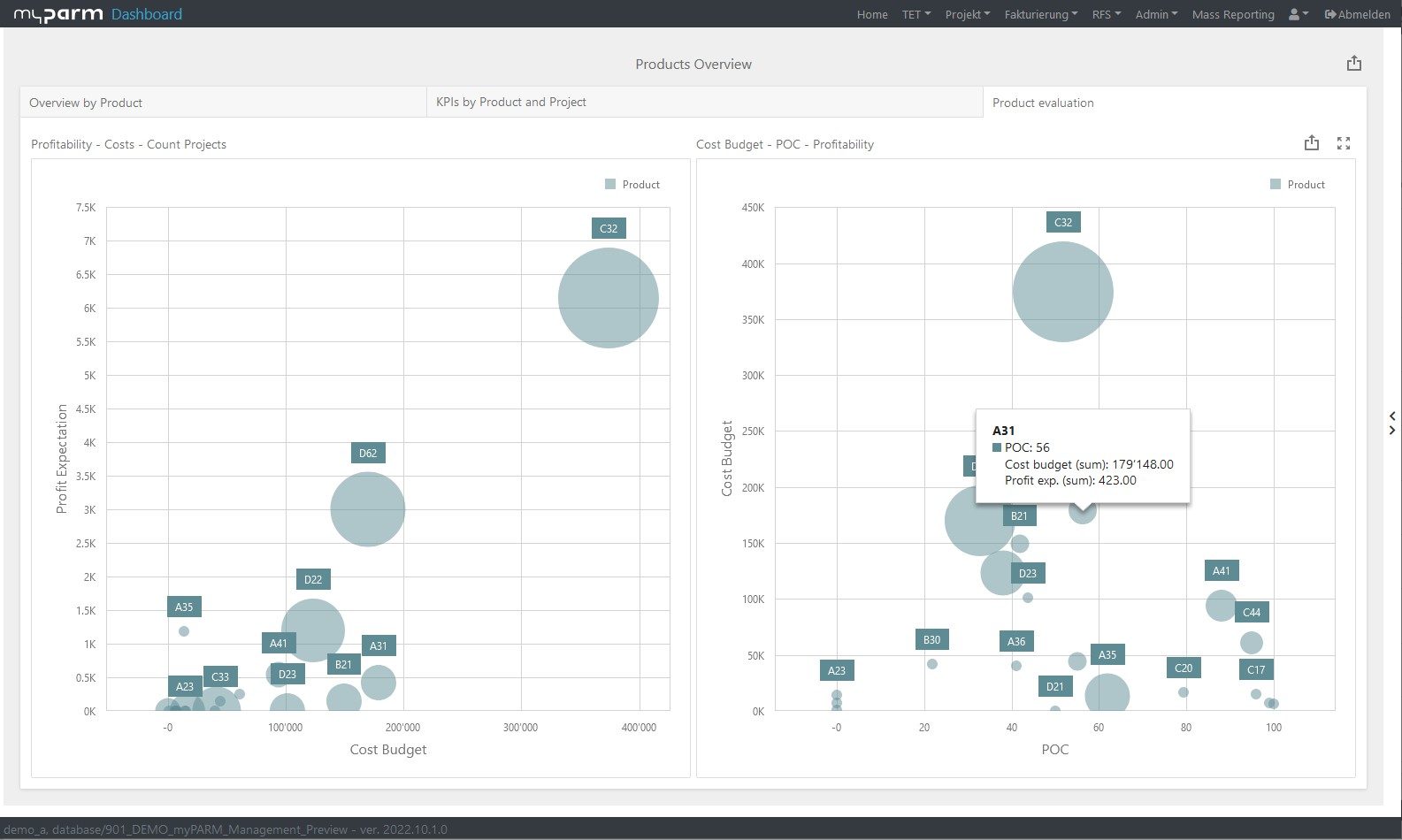
A look at your cash flow, balance sheet and income statement will show you whether your business is financially sound. Your liquidity indicates whether you can meet the needs of your business with the cash you have and thus helps you determine whether you can finance planned business growth, for example. If you put your turnover in relation to your profit, for example, you can use the return on sales to check whether your business is growing as planned.
2. Marketing key figures
Marketing indicators tell you whether your marketing campaigns are achieving the desired success. These include, for example, the conversion rate, which shows how well a marketing campaign is received by the target group. The customer acquisition costs, on the other hand, show you the ratio of the marketing budget spent on a new customer to the revenue generated by it.
3. Sales indicators
The sales ratio indicates how much money you invest in sales and how high the generated turnover is in comparison. The cancellation rate shows how many orders have been cancelled, while the closing rate shows how many orders have followed up on created offers. You can also measure metrics such as the complaint rate, which shows how satisfied your customers are with your products.
4. Project management key figures
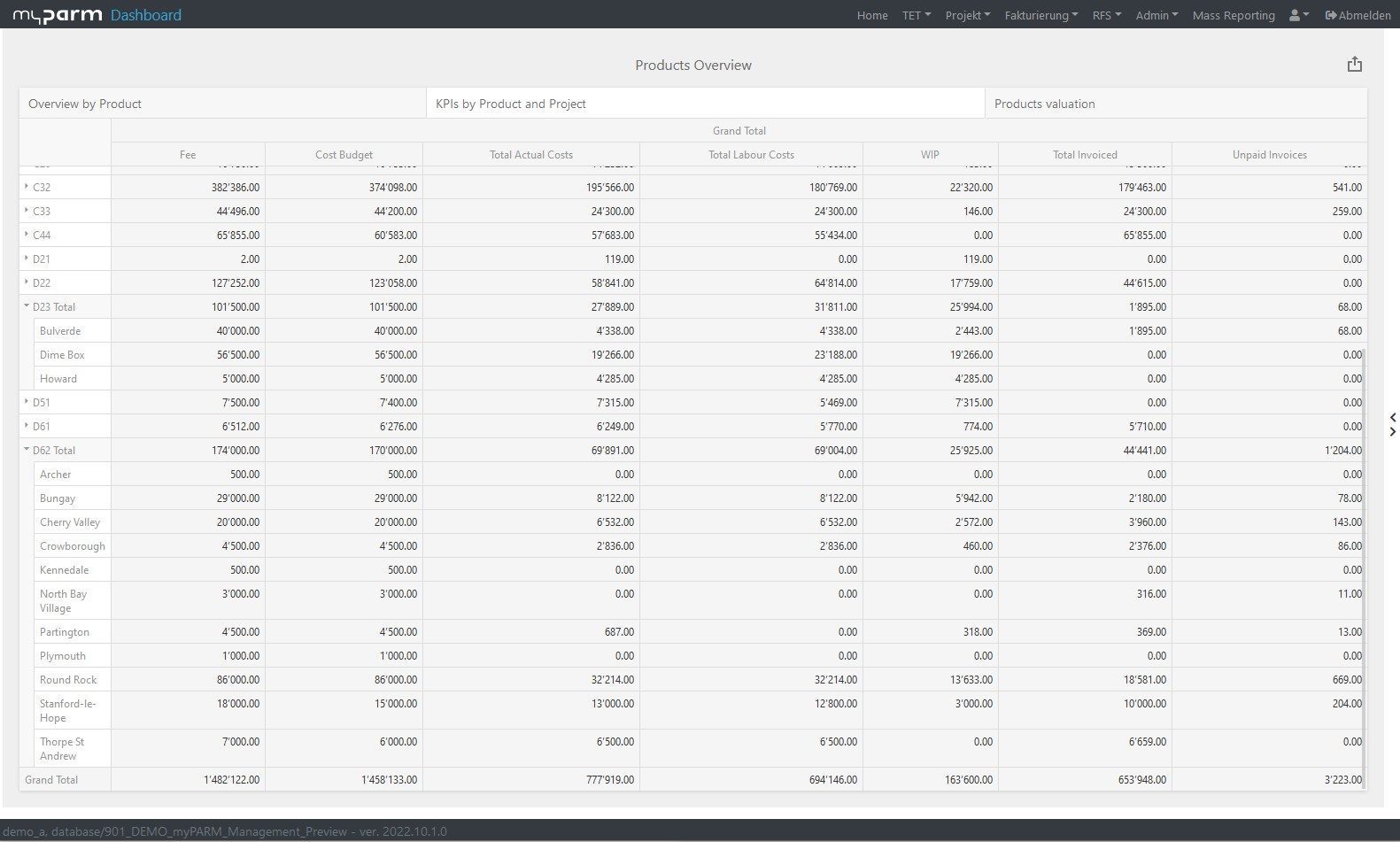
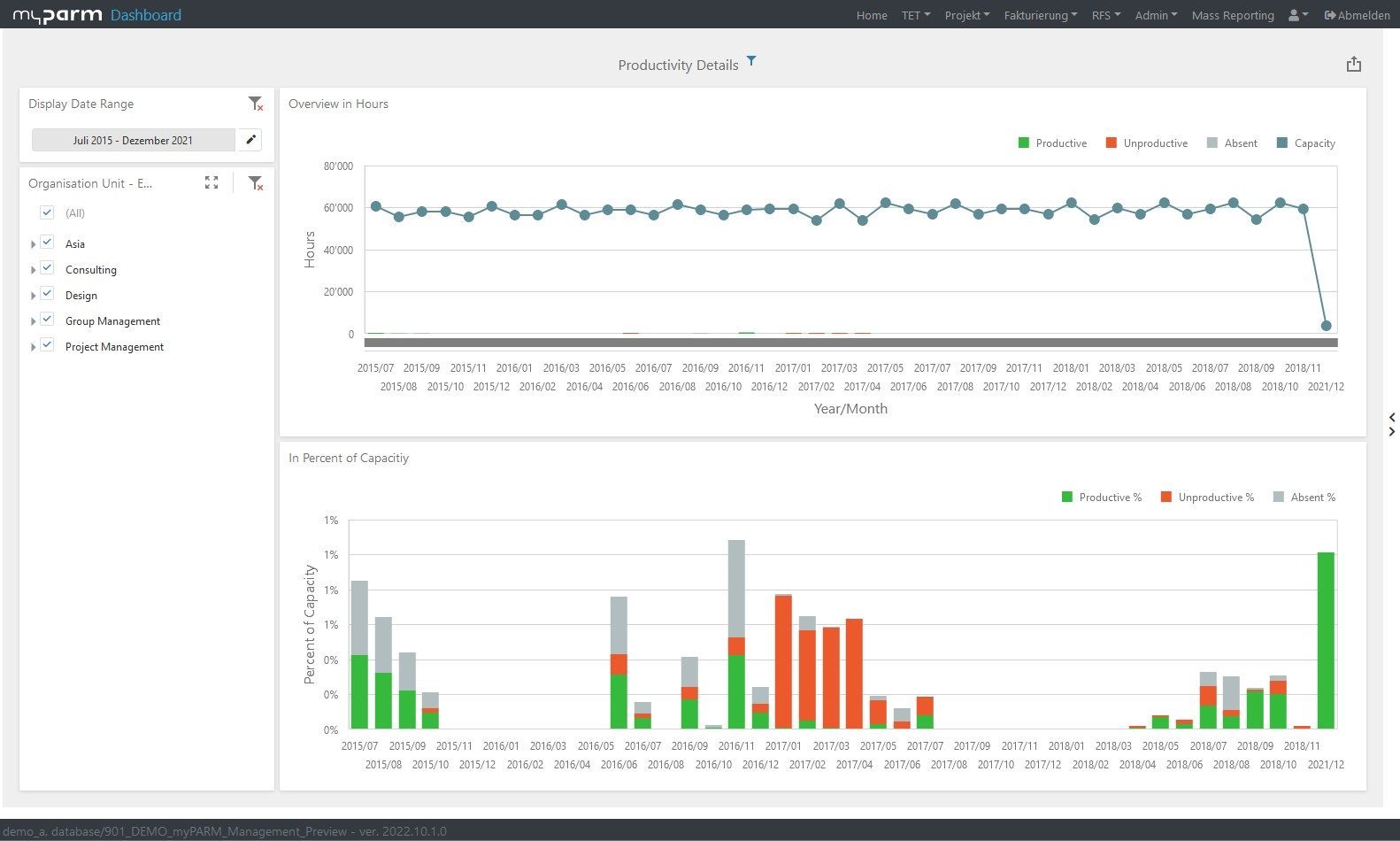
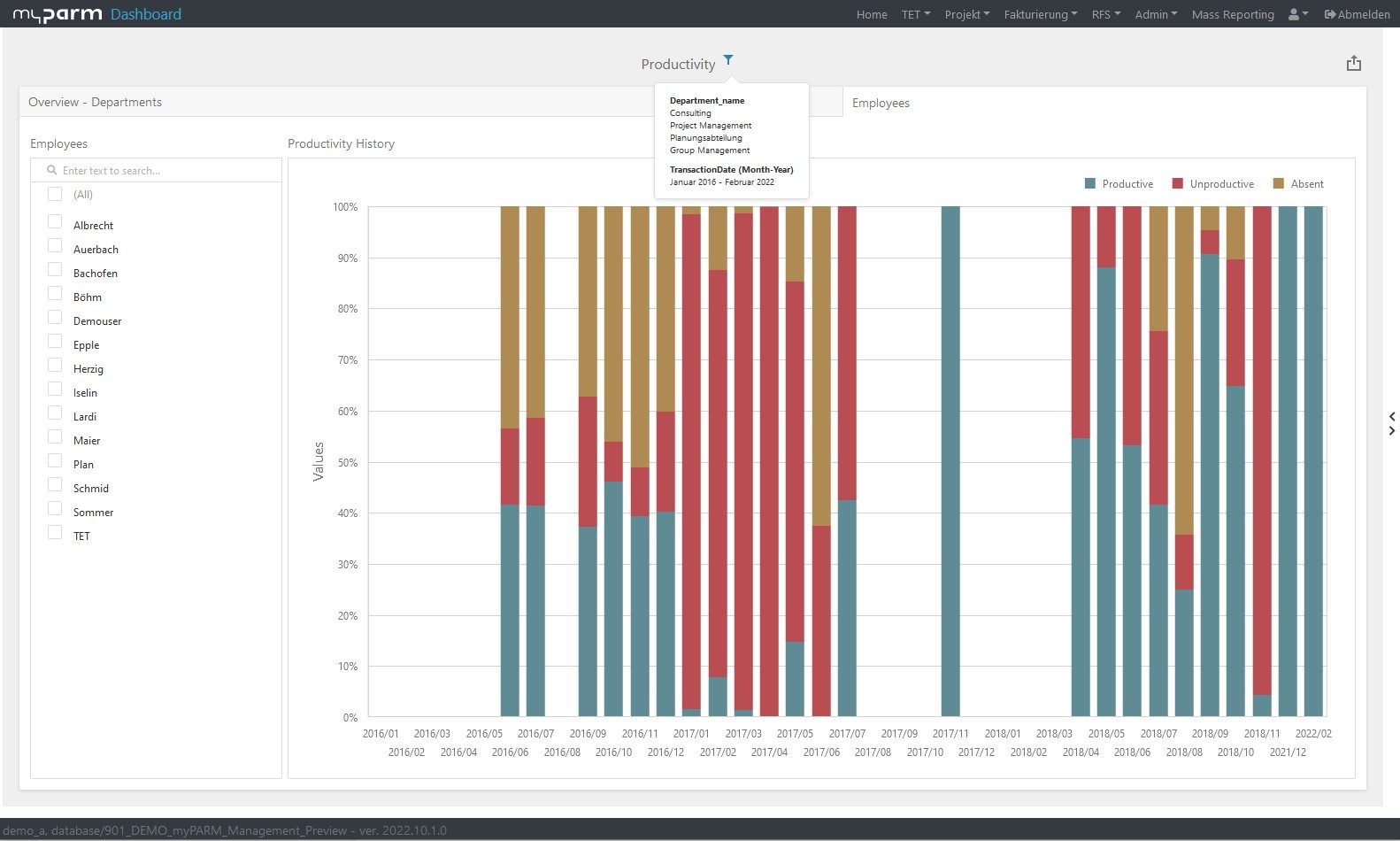
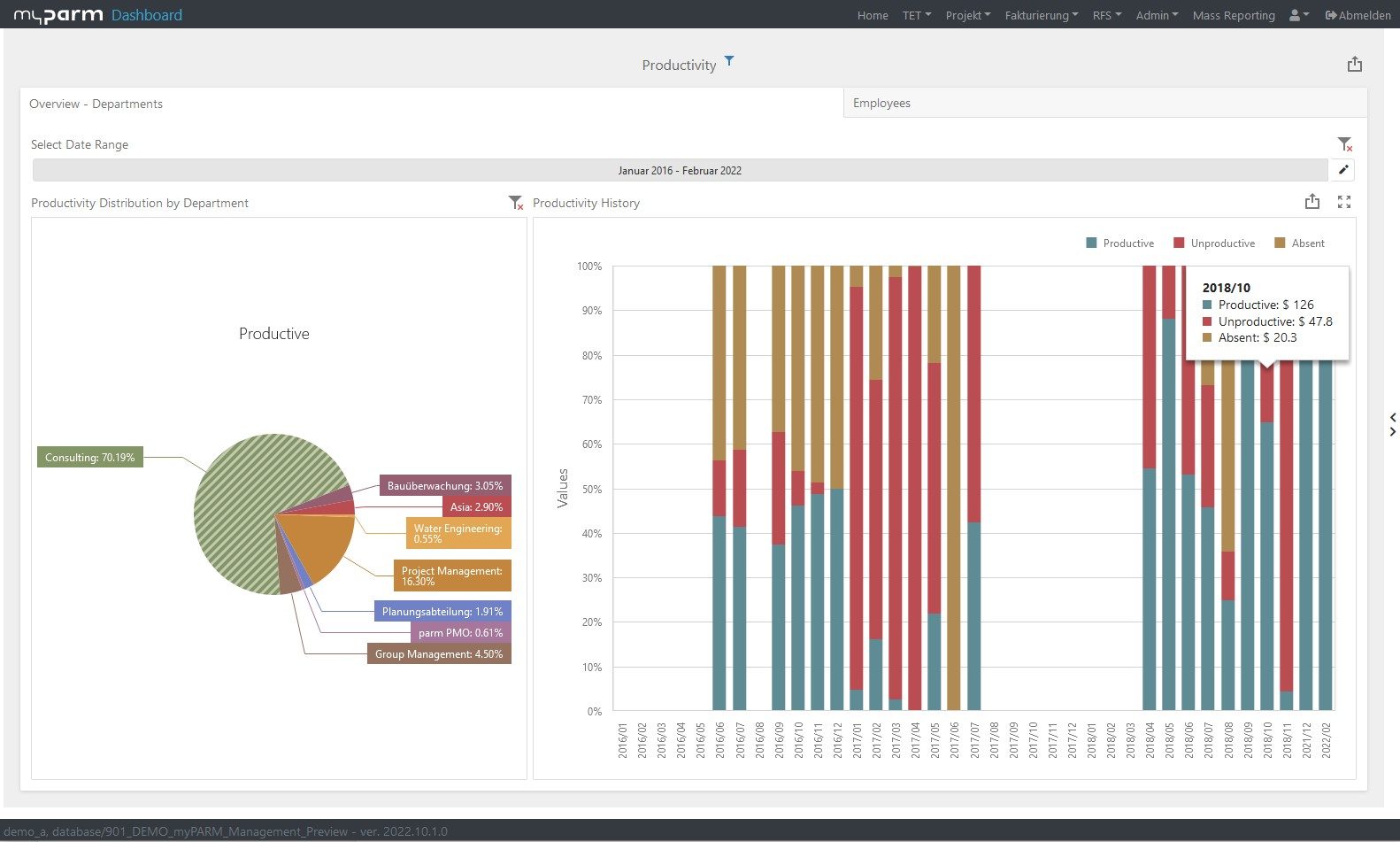
If your projects are completed on time and within budget, these are already important indications that your project management is working very well. But if you want to see whether project management performance has improved and what the projects have contributed to the fulfilment of your business strategy, you need other key figures. Productivity, for example, shows you how effectively the resources at your disposal have worked. Return on investment (ROI), on the other hand, tells you how much a project has paid off for your company, because it lets you know how much profit your investment in the project has brought you.
5. Key figures in production
In addition to easily ascertainable key figures such as production volume, production losses, production costs or even production time, you can also calculate, for example, plant effectiveness, which puts the factors of plant availability, performance and quality in relation to each other. Key figures such as the return rate give you an insight into the quality of your production. In addition, you can, for example, overview the unit costs over time.
6. Key figures in human resources
These key figures provide information on how your employees contribute to the health of your company, whether you are able to retain good employees, how attractive your company is as an employer and how satisfied your employees are. The performance and productivity of your HR team can also be analysed so that you know which processes and strategies are working. Cost per hire, for example, is a simple measure of how much you have spent on recruiting and hiring a new employee. Putting your profit in relation to the number of employees gives you the net profit per employee. This value gives you an idea of how efficient and productive your employees are. You can improve this value by investing in new technologies that make work easier or by training employees, for example in time management methods such as the Pomodoro Technique, so that they perform better.
Monitor the progress of key figures with BI
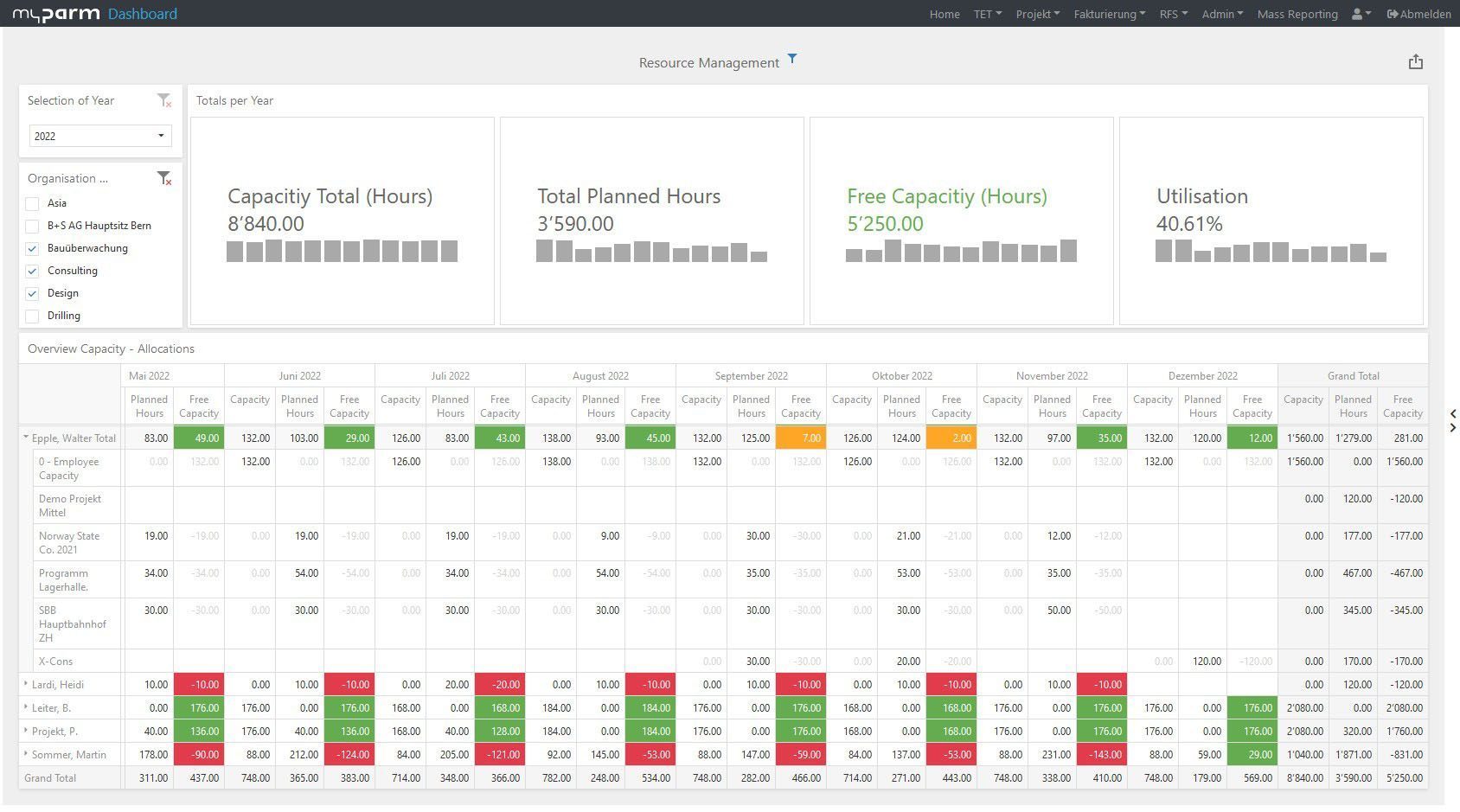
Once you have set the right metrics and goals, break them down to individual departments or employees. Think carefully about how a department can contribute to achieving your goals. If your goal is to maximise profits, for example, the production department can contribute by increasing productivity or redesigning production processes to reduce manufacturing costs. Purchasing, on the other hand, could contribute to the goal by finding cheaper suppliers for raw materials and thus increase profits, while sales could increase the closing ratio. Here, too, business intelligence can provide you with important clues to the right key figures, as with their help you can quickly see where there is still room for improvement.
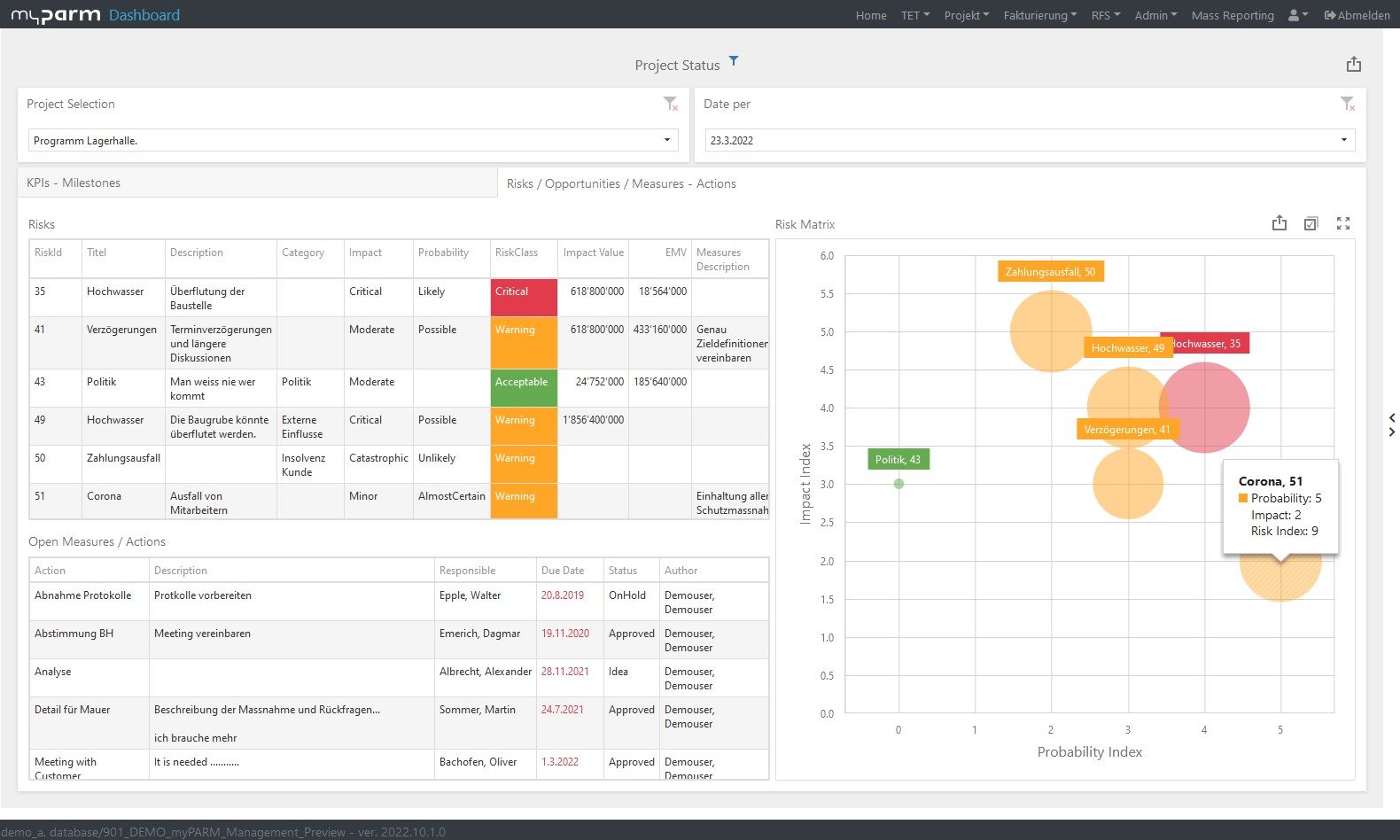
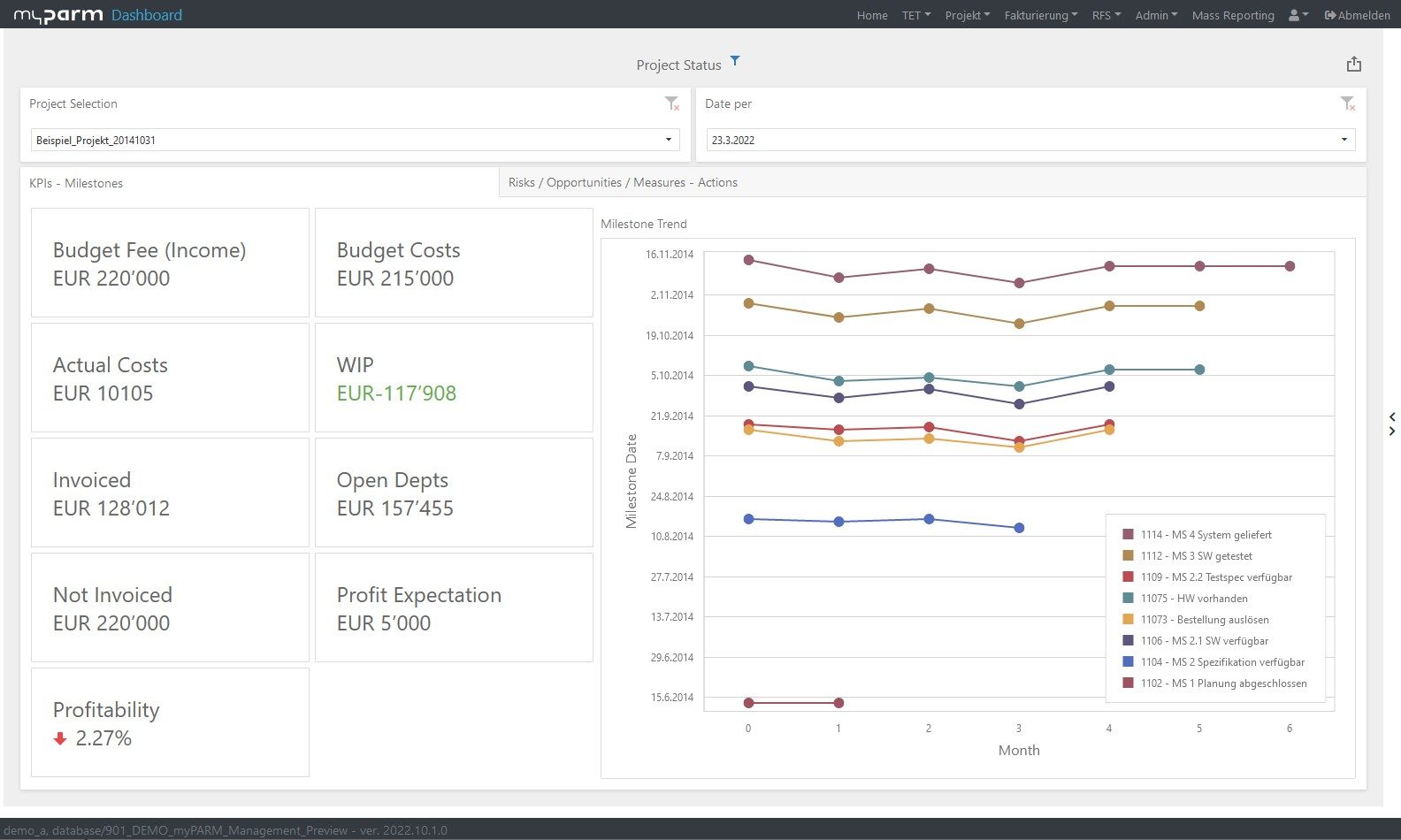
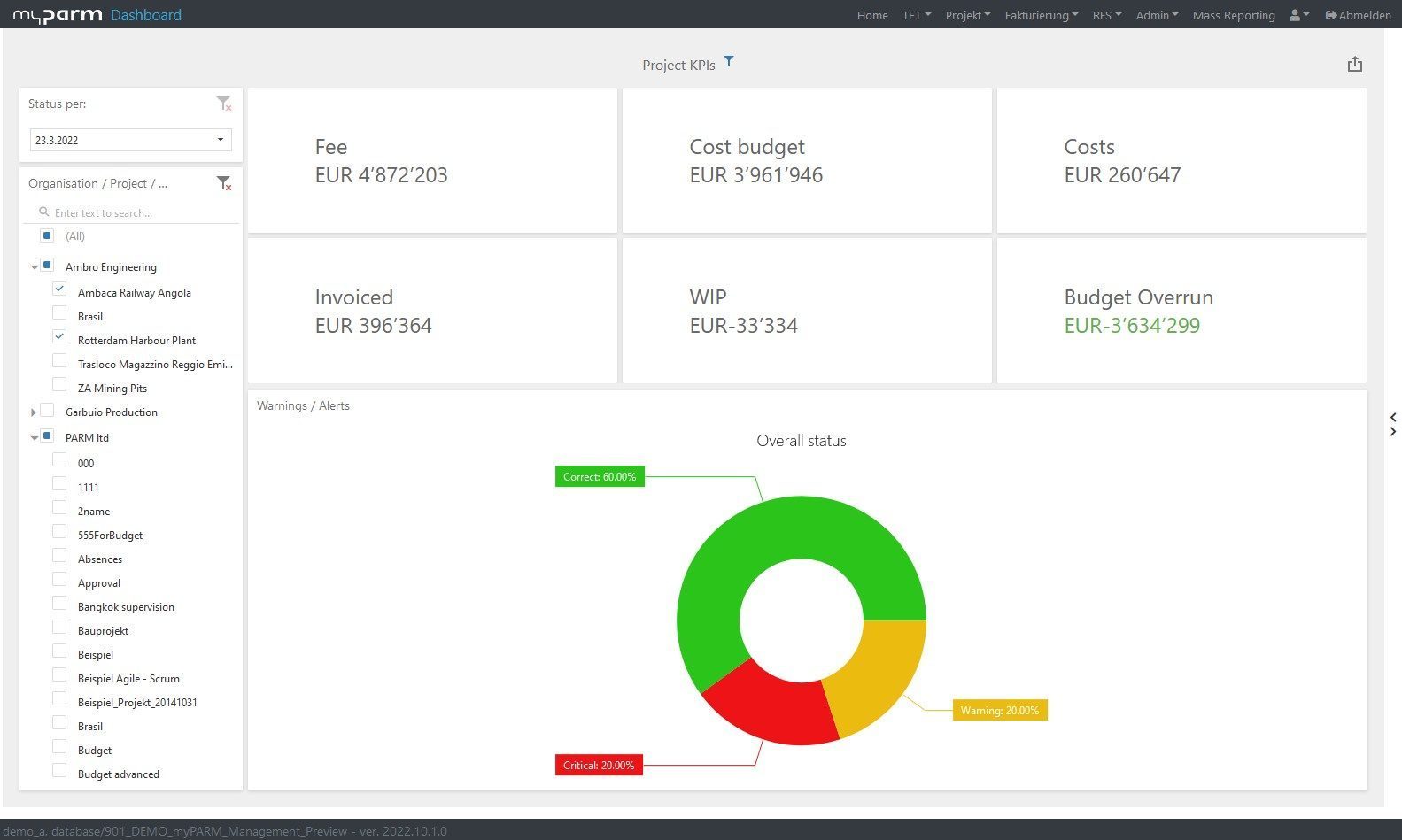
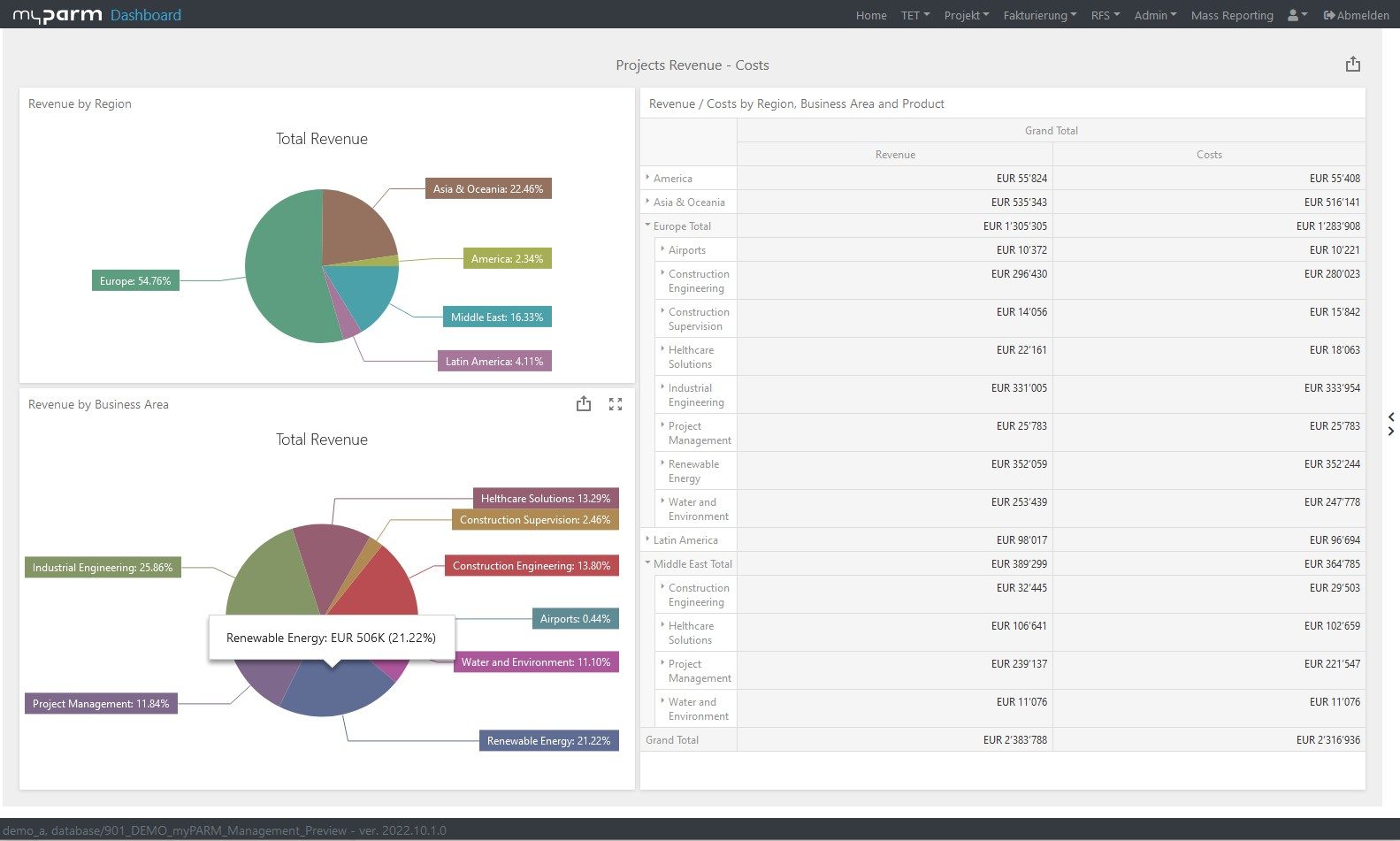
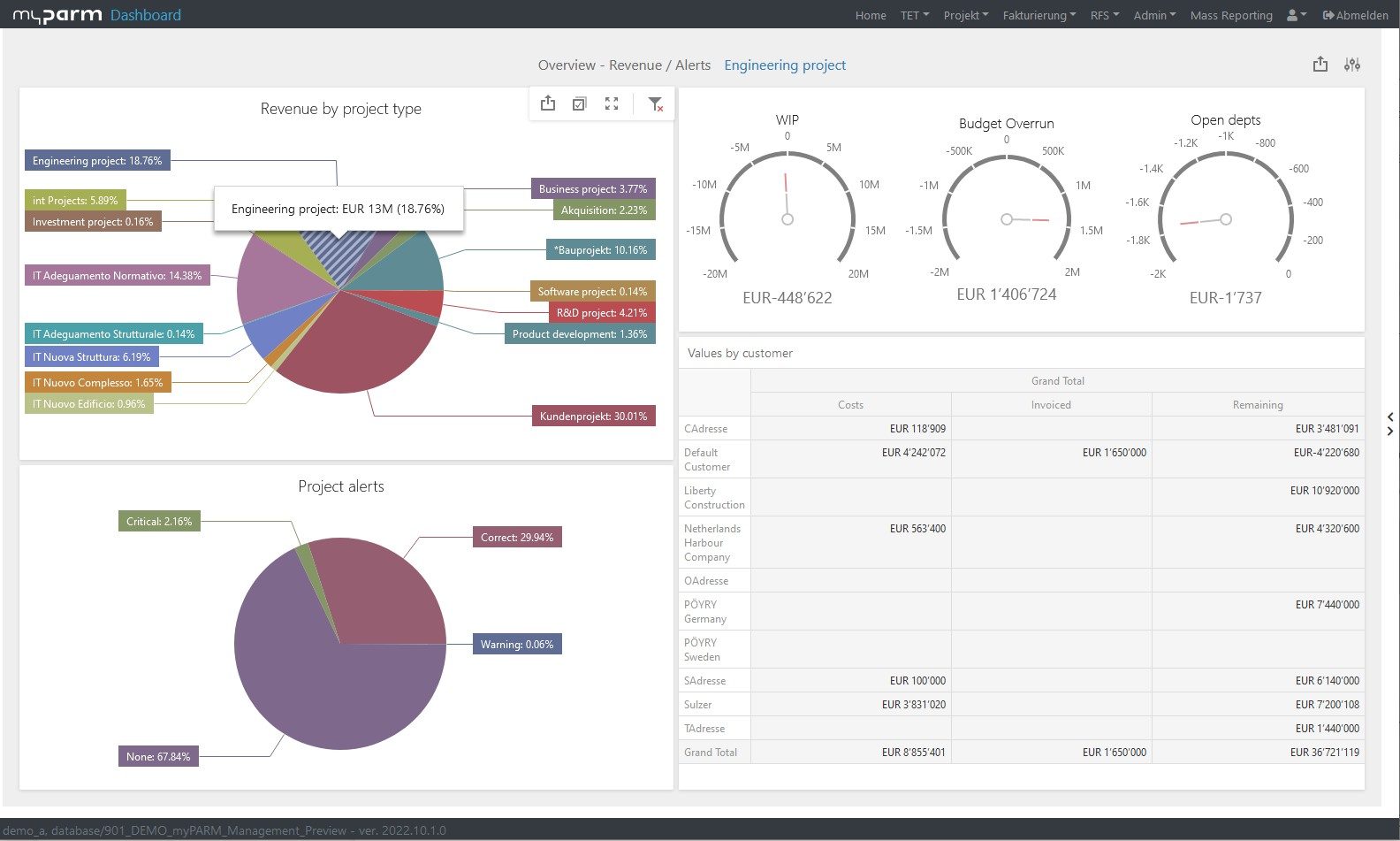
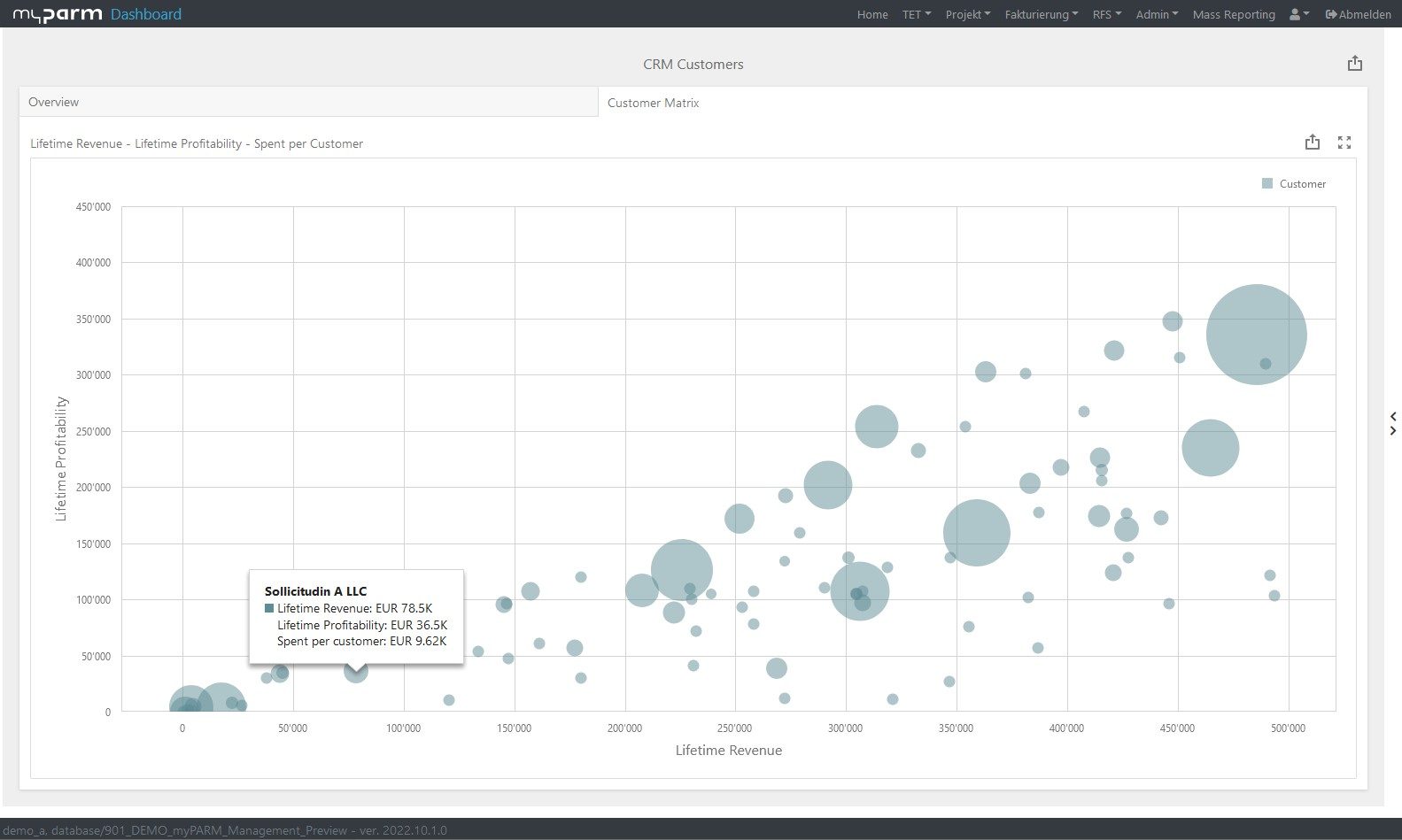
To constantly monitor the progress of the achievement and thus check how far your company has progressed in the implementation of the strategy, reports and dashboards adapted to the respective goals help. In this way, you give each department the opportunity to check their individual progress at any time. BI software with flexibly customisable dashboards can help you here, showing each department, manager and employee exactly the analyses that are relevant and visually presenting the KPIs, for example, in comparison with their development over time.
Conclusion
To ensure that all employees in your company pull together, a good corporate strategy is important. With the right, individually broken down KPIs, you support the achievement of goals and can check the progress in customised dashboards of your BI tool.
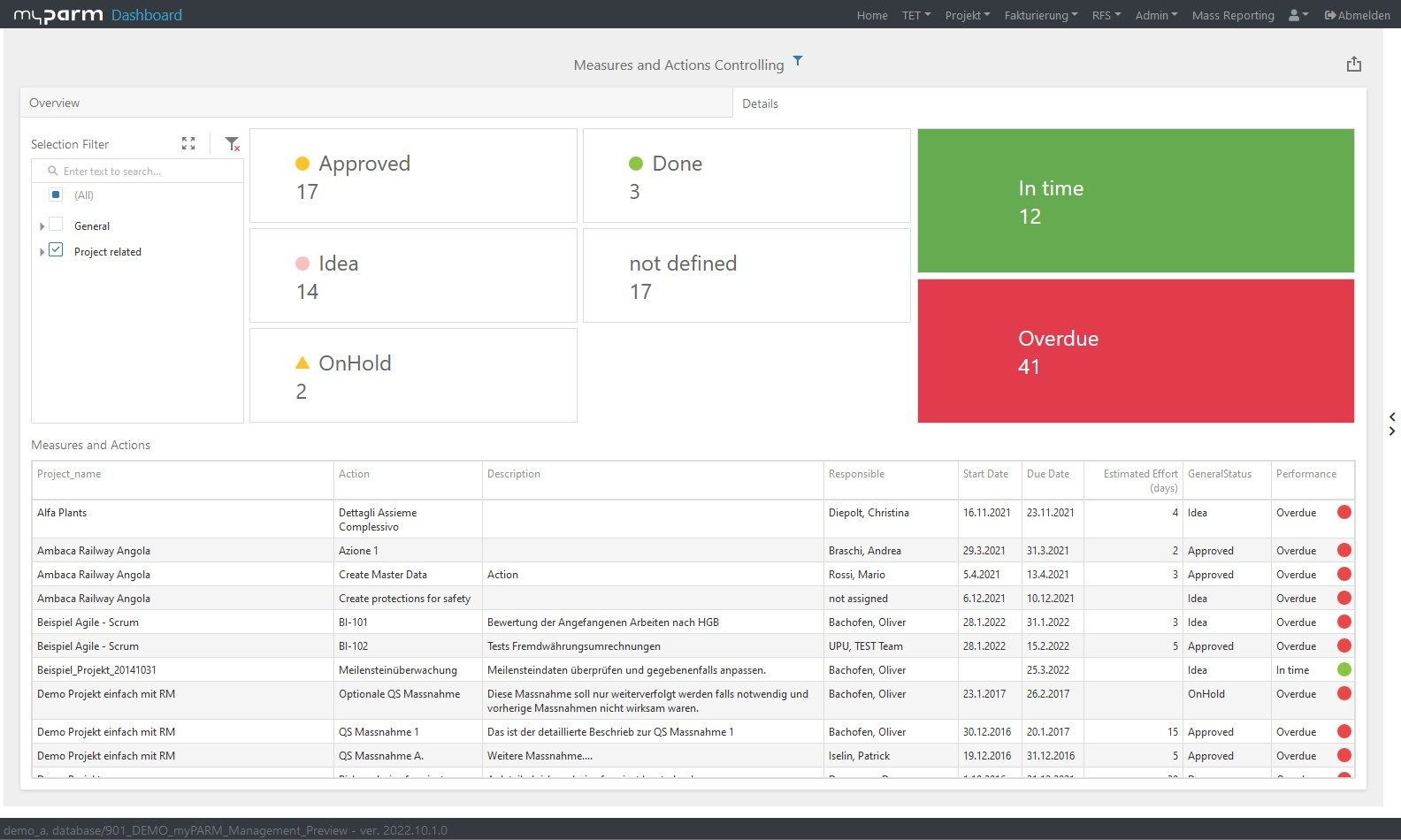
So a good BI software not only helps you to set the right business strategy and translate it into measurable goals, but also brings together all the important data so that you can always keep an eye on the relevant key figures according to your needs. An integrated balanced scorecard is ideal for mapping the corporate strategy in the software as well as for checking the status later. Ideally, BI software also allows you to create and monitor measures for achieving goals in the same system. With integrated task management, tasks can be passed to your team, allowing you to manage the actions of your business strategy. At the same time, this allows you to monitor the status of tasks, adjust actions if necessary, and communicate with your team through the system. In this way, a policy deployment method such as Hoshin Kanri can also be implemented in our system.
Learn more about the Business Intelligence Software Software myPARM BIact:
Would you like to get to know myPARM BIact in a demo presentation? Then make an appointment with us right away!