The digital control center of modern management: the management information system (MIS)

As a manager, you have to make decisions every day.
These could be very simple decisions, but also extremely complex ones that are not easy to make.
However, with the right data as a basis, it is possible to make optimal decisions.
Many managers obtain this data from a management information system (MIS).
We explain why an MIS forms the backbone of modern corporate management and why managers should never do without such a powerful tool.
What is a management information system?
A management information system is much more than just software – it is the digital nervous system of a company.
In principle, an MIS is like an omniscient assistant that provides you with exactly the information you need to make strategic decisions.
In other words, it is a computerized system that collects and processes company data from various sources and converts it into meaningful reports.
In this way, an MIS acts as a bridge between the operational systems that control day-to-day business and the management level that makes strategic decisions.
The evolutionary history of MIS
The history of MIS is closely linked to the development of computer technology.
In the 1960s, when computers were still room-filling behemoths, companies began to use them for simple tasks such as budgeting and order management.
Over time, the systems became more and more sophisticated.
In the 1970s and 1980s, more advanced database technologies enabled more complex analyses.
The 1990s brought a revolution in data networking with the advent of the internet.
Today, in the age of big data and artificial intelligence, MIS have evolved into highly complex, predictive systems that can not only analyze data, but also predict future trends.
Core tasks of an MIS
- Data collection and management: A modern MIS collects data from all areas of the company in real time.
From sales figures and production statistics to customer feedback – nothing escapes its watchful eye.
However, the real art lies in integrating these different data sources.
An effective MIS harmonizes data from ERP systems, CRM platforms, financial software, project management systems and many other sources into a coherent overall picture. - Data analysis and reporting: The MIS then transforms from data collector to data analyst.
It distils valuable insights from the mass of raw data.
Modern MIS systems use advanced analysis methods such as data mining, statistical modeling and machine learning to identify patterns and predict trends.
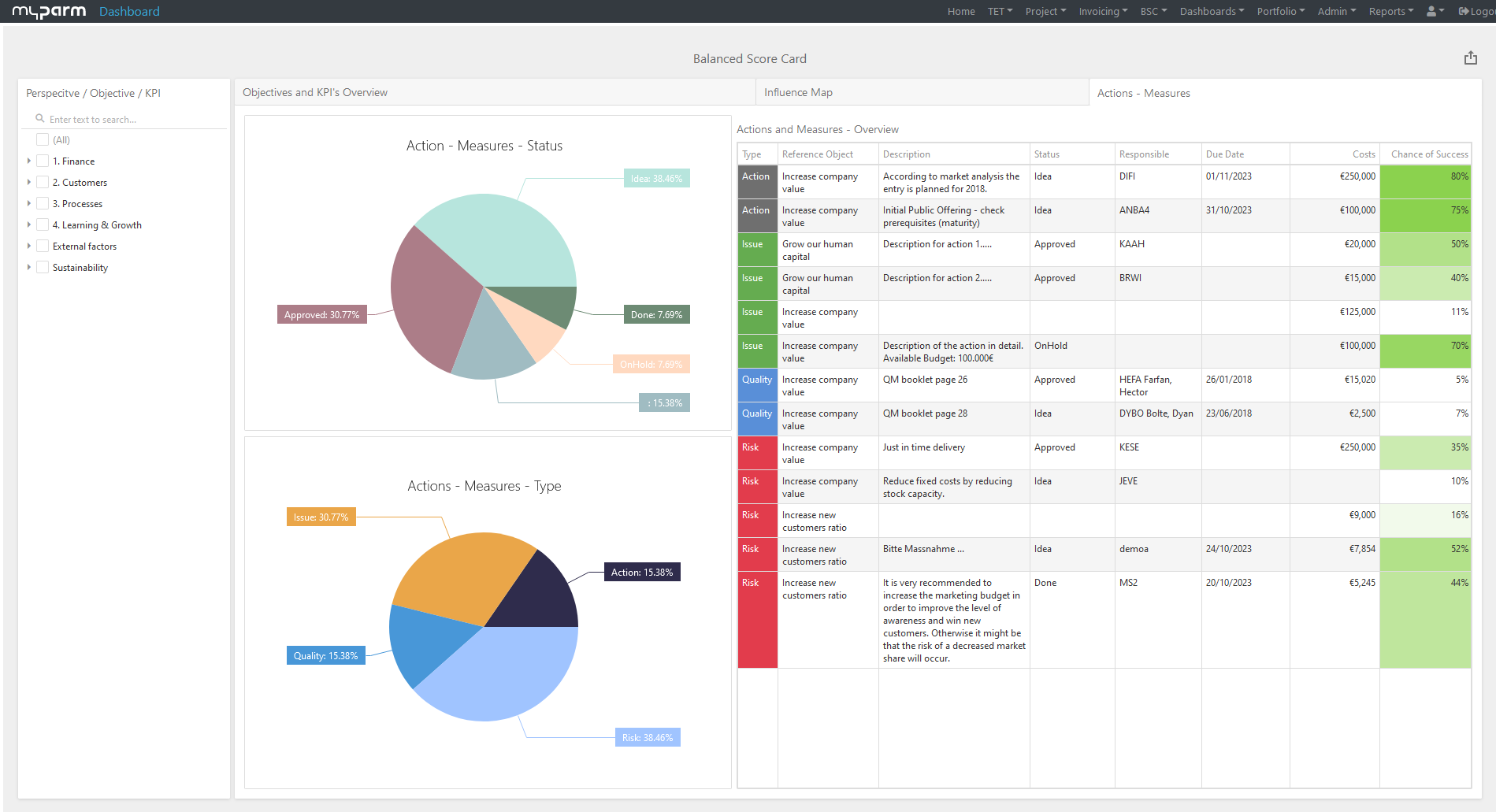
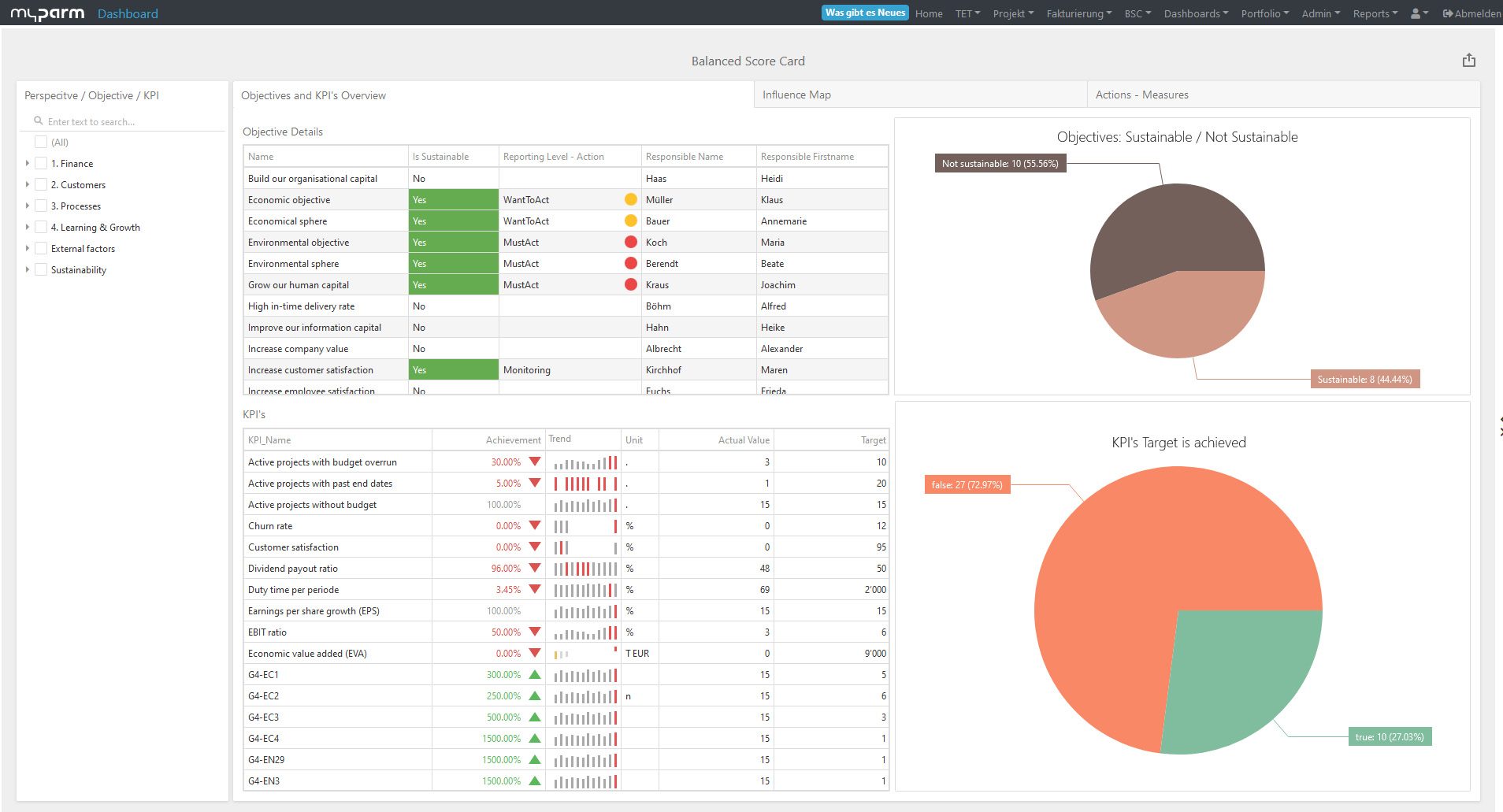
Reporting often takes the form of dashboards – clear visualizations that show the status of key metrics at a glance.
These can range from real-time displays of sales figures to complex financial forecasts or an early warning system for risks and difficulties. - Decision support: The data collected and analyzed by the MIS serves as a strategic advisor to the management level.
Some MIS not only provide data and context-related analyses, but can also make direct recommendations for action.
For example, if sales figures are falling in a certain region, such an MIS could not only point out the underlying problem, but also analyze possible causes (e.g. increased competition or demographic changes) and suggest solutions.
Advantages of an MIS
The advantages of a management information system are obvious.
On the one hand, the system provides an information advantage that enables managers to make decisions quickly.
This speed can be decisive for the success of a company and can at least give the company an advantage.
For example, it is possible to react very quickly to market changes or new customer requirements.
On the other hand, an MIS breaks through information silos and thus provides a holistic overview of the company.
This prevents important correlations from being overlooked and promotes a holistic understanding of business dynamics.
By automating data collection and analysis, an MIS also drastically reduces the time required to gather information.
This allows managers to focus on interpreting the data and making decisions, enabling them to work more efficiently.
An MIS can also help to minimize risk.
By highlighting potential problems at an early stage, an MIS helps to anticipate and manage risks.
For example, it can predict supply bottlenecks or draw attention to changing market conditions.
MIS in action
To illustrate the practical importance of an MIS, let’s look at an example from the logistics industry: Imagine you are the CEO of a global logistics company.
Your MIS shows you a central dashboard:
- The utilization of your fleet in real time, broken down by region and vehicle type.
- Fuel consumption and costs, with forecasts based on current market trends.
- Delivery times and customer satisfaction values, with warning messages in the event of deviations from target values.
- Market analyses that identify competitive activities and potential new business areas.
With this information, you can make informed decisions, such as
- Plan investments in new, fuel-efficient vehicles.
- Optimize routes based on traffic and weather data in real time.
- Adapt pricing strategies to market conditions and customer demand.
- Develop new services to take advantage of emerging market opportunities.
The future of MIS
The future of MIS promises to be as exciting as it is transformative.
With advances in areas such as artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things (IoT) and quantum computing, management information systems will become even more powerful and proactive.
Imagine an MIS that not only analyzes data but also makes autonomous decisions – such as a system that automatically adjusts inventory levels or optimizes marketing campaigns.
Or think of an MIS that understands natural language and can answer complex business questions as if it were a human expert.
The integration of augmented and virtual reality could revolutionize the way we interact with data.
This could allow you to “walk” through a virtual representation of your business data and recognize patterns that would remain hidden in traditional 2D representations.
Conclusion
A management information system is far more than just a technological tool – it is a strategic partner for your company.
It transforms the huge flood of data that most organizations collect every day into a clear stream of insight that helps you navigate the turbulent waters of the business world.
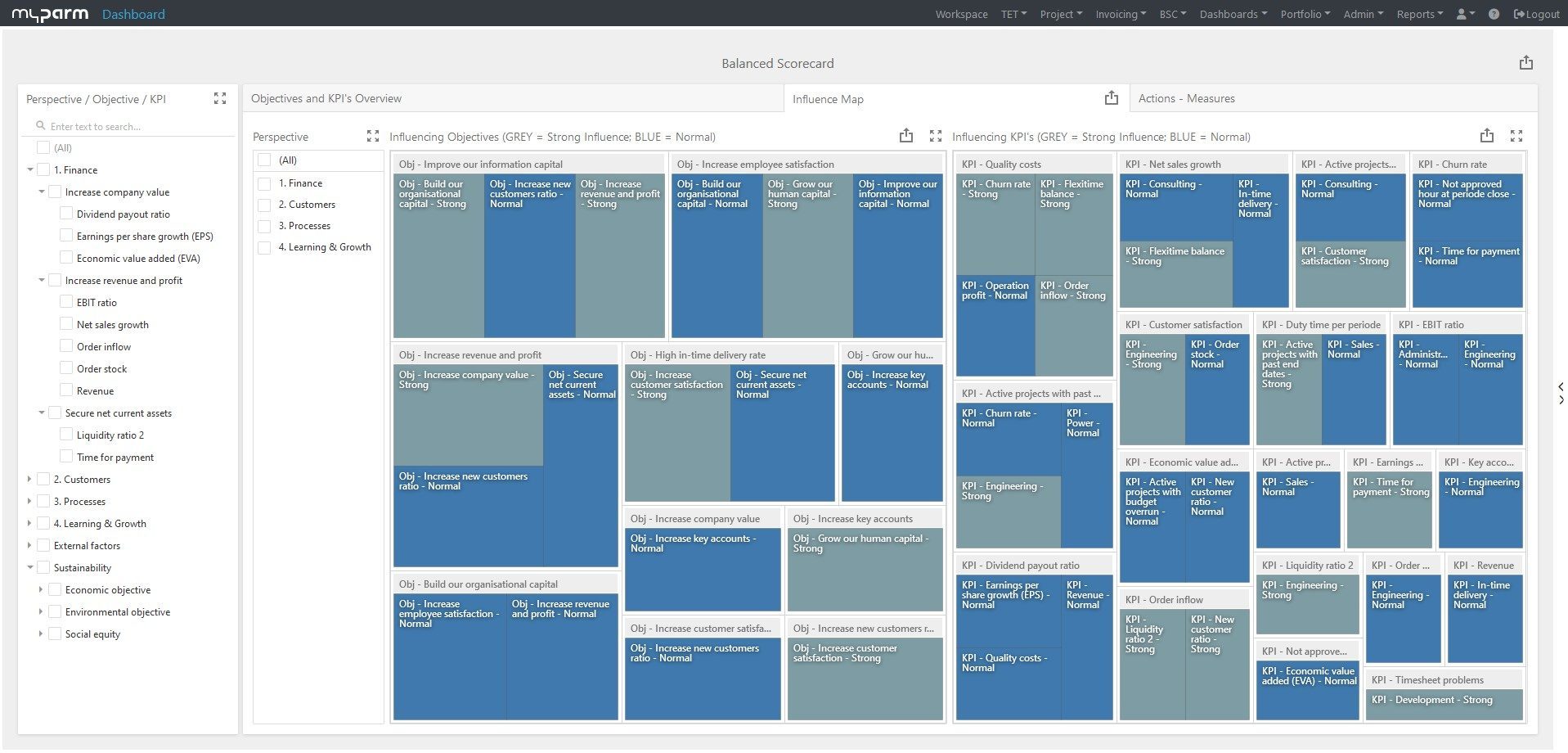
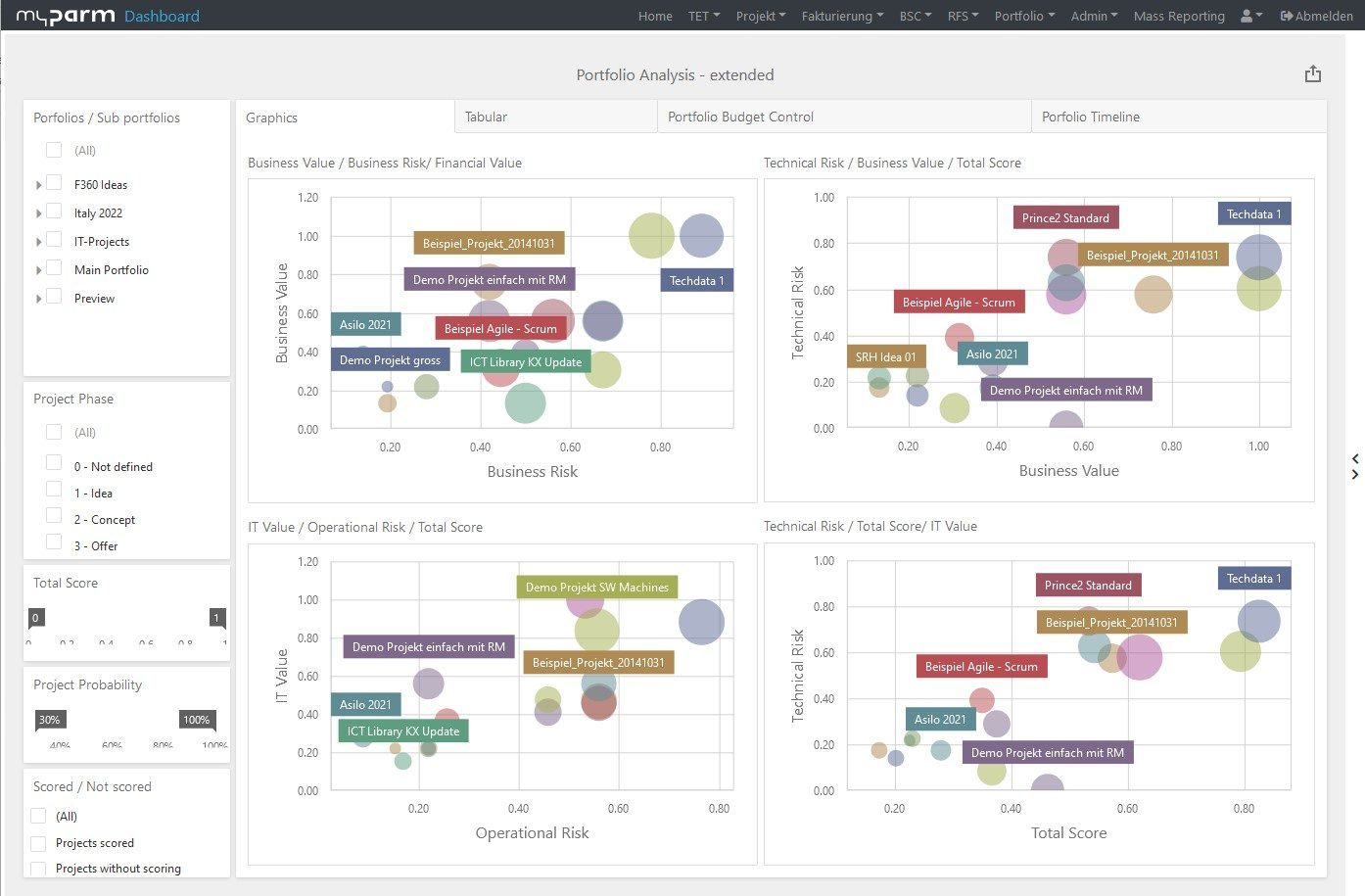
The myPARM CorporateNavigator management software includes an MIS that offers managers a holistic view of their company.
With additional functions such as a balanced scorecard for strategy development and implementation, strategic portfolio management and risk and opportunity management, myPARM CorporateNavigator supports decision-makers in managing their company effectively and making it future-proof.
The additional task management function also helps to assign strategic tasks directly to employees, monitor their status and thus track the successful implementation of the strategy.
Find out more about the myPARM CorporateNavigator leadership software:
Would you like to get to know myPARM CorporateNavigator in a demo presentation? Then make an appointment with us right away!