Project Management ABC: P for Project Portfolio Management
The key to successful project management

When selecting projects, it can be difficult to keep track of what’s going on and ensure that the projects you choose align with your company’s strategic goals. Project portfolio management offers a solution to these challenges. It enables companies to select, prioritise and monitor projects to ensure that resources are used effectively and projects are completed successfully. In this blog post, we will take a closer look at project portfolio management and see how it can help organisations to complete their projects successfully.
What is project portfolio management?
In a rapidly changing environment and economy, it is essential for companies to effectively plan, monitor and manage their projects to achieve the company goals. Project portfolio management is an integral part of any successful business strategy as it helps companies select projects that best support the business strategy.
Project portfolio management (PPM) is, therefore a systematic approach to optimising the selection, control, and monitoring of projects within a company. The goal of PPM is to maximise the company’s overall performance through the effective use of available resources. This is achieved by selecting projects that best support the corporate strategy as well as by carefully planning and managing resources. Monitoring and controlling projects is also essential to ensure that they meet the company’s strategic objectives and that adjustments can be made if necessary.
- Identifying corporate goals
- Collecting project requests and ideas
- Evaluating, prioritising, selecting, initiating and rejecting projects
- Analysing dependencies between projects
- Monitoring and controlling the portfolio as well as the individual projects
- Evaluating completed projects
Thus, PPM enables companies to plan, monitor and control their projects more effectively to achieve their goals. This minimises risks, optimises the use of resources and ensures that projects meet the company’s strategic goals.
Differences between multi-project management, programme management and project management
- Project portfolio management (PPM): PPM refers to managing and monitoring all projects within a company or organisation. It helps companies align their projects with strategic goals, prioritise projects and use resources effectively.
- Program management: Program management refers to the control and monitoring of a group of projects that are grouped together to achieve common goals. So it relates to the totality of projects that are grouped together to achieve a larger goal.
- Multi-project management: Multi-project management refers to the control and monitoring of several projects simultaneously. It refers to the ability to successfully plan, execute and complete multiple projects simultaneously.
- Project management: Project management refers to controlling and monitoring a single project. It therefore refers to the ability to successfully plan, execute and complete one project.

Application examples
- IT industry: For numerous potential IT projects, PPM helps with selection, planning, prioritisation, and monitoring so that the selected projects are in line with the company’s business objectives. This is particularly necessary as the IT industry suffers from a severe labor shortage with the required skills. So, with a good PPM, the available professionals can work on projects that optimally support the company’s success.
- Construction industry: In the construction industry, PPM helps to make the most effective use of the resources needed while ensuring that construction projects meet the client’s requirements. As construction projects often have a very long implementation phase of several years, a lot can change during this time. Project portfolio management helps companies in the construction industry to keep an eye on the big picture, even in this case while keeping the goals in mind.
- Pharmaceutical industry: In drug or therapy development, PPM can be used to plan, prioritise and monitor projects. In this way, it helps to implement the development strategy successfully.
- Financial industry: PPM can also be used in the financial sector to implement a financial strategy with suitable projects and thus achieve business goals. Portfolio management thus helps companies in the financial sector to keep an eye on their projects’ performance and adapt to trends.
How does project portfolio management work?
Project portfolio management usually involves five steps that are closely linked:
1. Identification of corporate goals:
In the first step, corporate goals and strategies are identified to ensure that the selected projects support them in the next steps. This includes analysing current and future business conditions as well as identifying opportunities and challenges.
2. Collecting requests and ideas:
Ideas for new projects come from different sources within a company. These ideas should be collected in a central place so that they can be evaluated in the next step. For this you can keep a simple spreadsheet, or enter the data into a project portfolio management software.
3. Selection of projects:
Once the corporate goals and strategies are established, projects are evaluated, and those that best support the corporate goals and strategies are selected. This is done using a standard company process with criteria such as strategic value, risk, time, resource requirements, and finances. As projects are evaluated, the criteria are applied individually to each project, and the results are then correlated. This helps to identify which projects are the most suitable. In this step, a ranking of the projects can also be made to simplify the selection and prioritise the projects. However, in this step, you should also bear in mind that the individual projects should be feasible and the portfolio as a whole. Thus, the selected projects as a whole should not be too big, too expensive, too risky, or too interdependent.
4. Resource planning:
In the next step, you can assign a project leader to the selected projects and thus initiate the projects. This includes allocating the necessary resources (staff, time, budget) for each project in the portfolio, considering the projects’ priorities, and the resources’ availability.
In PPM, resource planning can be done roughly, leaving the project manager to do the detailed planning. Nevertheless, resource planning is an important part of PPM to ensure that resources are used effectively. During project implementation, resource planning should also be continuously monitored so that it can be adjusted if necessary. This may require resources to be diverted from one project to another to ensure that a higher priority project can be successfully completed.
5. Monitoring and control:
Projects evolve over time and new ideas can appear at any time. Therefore, it is important to continuously review both the progress of the projects as well as the new project ideas and make adjustments if necessary. This ensures that projects are implemented successfully and that they still meet the strategic goals of the company, even if some time has passed since they were selected and planned. Frequent project reports and project status meetings allow all stakeholders to stay up to date on the implementation of the projects in your portfolio and to react, for example, to new risks or opportunities.
6. Reporting and communication:
The preparation of project status reports is also of crucial importance. These should be regularly shared with management and other interested parties to document the progress, performance and expenditure of each project. These reports help management to react quickly to changes and make necessary adjustments. Only by communicating properly will you ensure that all stakeholders are aware of the progress as well as the results of the projects, and that any issues can be addressed quickly.
How can projects be evaluated?
In project portfolio management, projects are usually evaluated against certain criteria to select those that best support the organisation’s strategic objectives. Some commonly used criteria are:
- Strategic value: How well does the project support the company’s strategy and contribute to achieving the company’s goals?
- Financials: What are the expected costs and revenues of the project, and how does it fit into the company’s financial budget?
- Risk: What are the risks associated with the project and how can these be minimised?
- Resource requirements: What resources are required for the project, and how readily available are they?
- Timing: How long will the project take, and does it fit into the company’s schedule?
- Potential for success: What is the probability that the project will be completed successfully?
The weighting of these criteria varies between companies and may also change over time. The criteria must be clearly defined and understandable so that all people involved can understand and apply them, as well as that the evaluation of projects is consistent and objective.
PPM in agile project management
Agile PPM is an approach that integrates the agile principles and methods of project management into project portfolio management. It uses agile approaches such as Scrum, Kanban and Lean principles to complete projects faster and more flexibly. This enables companies to react quickly to changes and better to adapt projects to the needs of the company.
In contrast to traditional PPM, where projects are planned and executed in long phases, the planning and execution of projects take place in shorter iterations and steps. For example, at the operational level, sprints are conducted every week, up to every four weeks, while at the tactical level, it can be two to three months, and at the strategic level, even one to two years. This allows companies to react more quickly to changes and better to adapt projects to the needs of the company.
However, it is important to note that Agile PPM is not suitable for every area of application and in some cases it may be more appropriate to use traditional project portfolio management methods.
Challenges of PPM
There are some challenges and risks related to project portfolio management:
- Insufficient resources: One of the biggest challenges is to provide enough resources (staff, time, money) for all projects. A lack of resources can lead to projects being delayed or not being successfully completed.
- Inadequate prioritisation: Another risk is that projects are not prioritised properly and resources are wasted on projects that have no strategic value.
- Difficulties in communication and collaboration: Project portfolio management requires close cooperation and communication between different departments and functional areas of the company. This can lead to difficulties when it comes to monitoring and controlling projects.
- Lack of transparency and traceability: Another risk is that it can be challenging to monitor and track the progress and performance of projects if there are no appropriate mechanisms and reporting procedures in place.
- Project selection risks: Poor selection of projects not aligned with business strategies can lead to wasted resources and time without a successful outcome.
- Insufficient adaptability: In fast-changing environments, it is important to be flexible to adjust projects and resource requirements accordingly when the business environment or strategic objectives change.
Advantages of PPM
- Ideal alignment of projects with corporate goals as well as projects with each other
- Improved resource management
- Risk reduction
- Better transparency
- Holistic planning of projects
- A clear basis for decision-making
Disadvantages of PPM
- High effort: Project portfolio management requires a lot of time and resources to select, prioritise and monitor projects.
- High cost: Project portfolio management can be expensive, especially if specialised software or consultants are needed.
- Potentially complex: Project portfolio management can be complex and requires a deep understanding of the business strategy and environment.
- Difficulty in implementation: Implementing the right project selection, resource planning and monitoring processes can be difficult, especially in companies with numerous departments and projects.
- Conflicts in resource allocation: Project portfolio management can also lead to conflicts in resource allocation, especially when allocating limited resources.
- Possible misunderstandings in collaboration: As project portfolio management requires collaboration and communication between different departments and functional areas, misunderstandings may arise that can affect the implementation and successful completion of projects.
Tips for applying PPM
To avoid potential difficulties with PPM, here are some tips and best practices:
- Clear objectives and strategies: It is important that business objectives and strategies are clearly defined so that projects that support them can be selected.
- Consistent criteria: Use consistent criteria to evaluate projects to ensure that all projects are evaluated fairly. Also make sure that all people involved understand and can apply these criteria.
- Resource management: It is important that resources (staff, time, money) are carefully planned and managed to ensure that they are available for the selected projects.
- Monitoring and control: Regularly monitor the progress of projects and make adjustments if necessary to ensure that projects continue to meet the strategic objectives of the organisation.
- Communication and reporting: Frequent reporting to management and other interested parties is necessary to keep everyone informed about the progress and performance of the projects.
- Flexibility and adaptability: Be flexible and adaptable to adjust projects and resource needs accordingly as the business environment or strategic objectives change.
- Project portfolio governance: Project portfolio governance defines the structure and procedures used to govern the selection, control, and monitoring of projects within an organisation. It includes the decision-making processes, policies, procedures, and responsibilities established for this purpose within the company. It also provides for the creation of mechanisms to monitor compliance with these rules and reporting mechanisms to monitor the progress and performance of projects. Effective project portfolio governance is important to ensure that the projects being implemented are in line with the company’s strategic objectives and that resources are being used effectively. In this way, it also helps to minimise risks and ensure that projects are completed successfully.
Conclusion
Project portfolio management can help you achieve the company’s goals and select the right projects to achieve them. It makes the basis for decision-making transparent and helps you to make the best use of available resources.
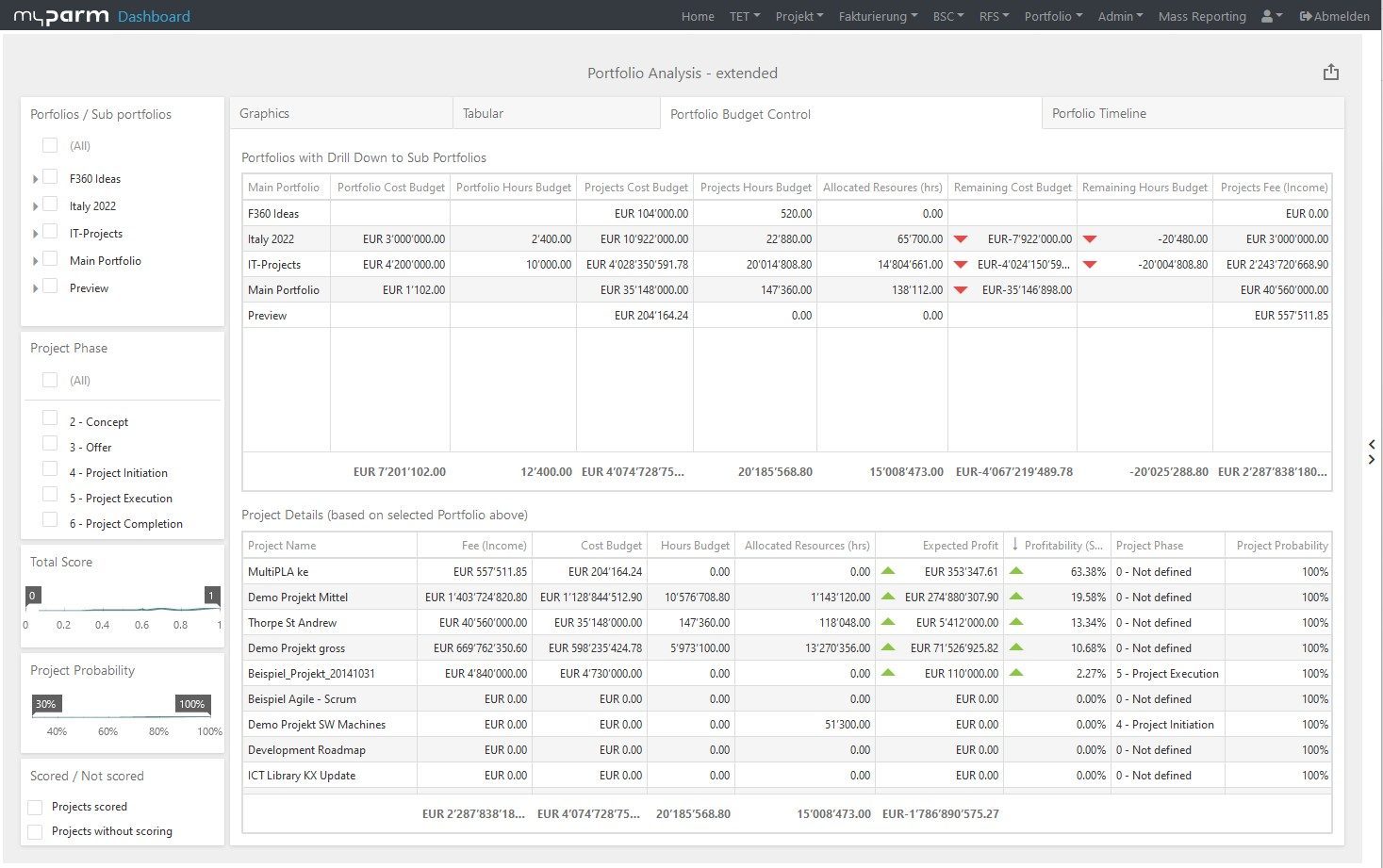
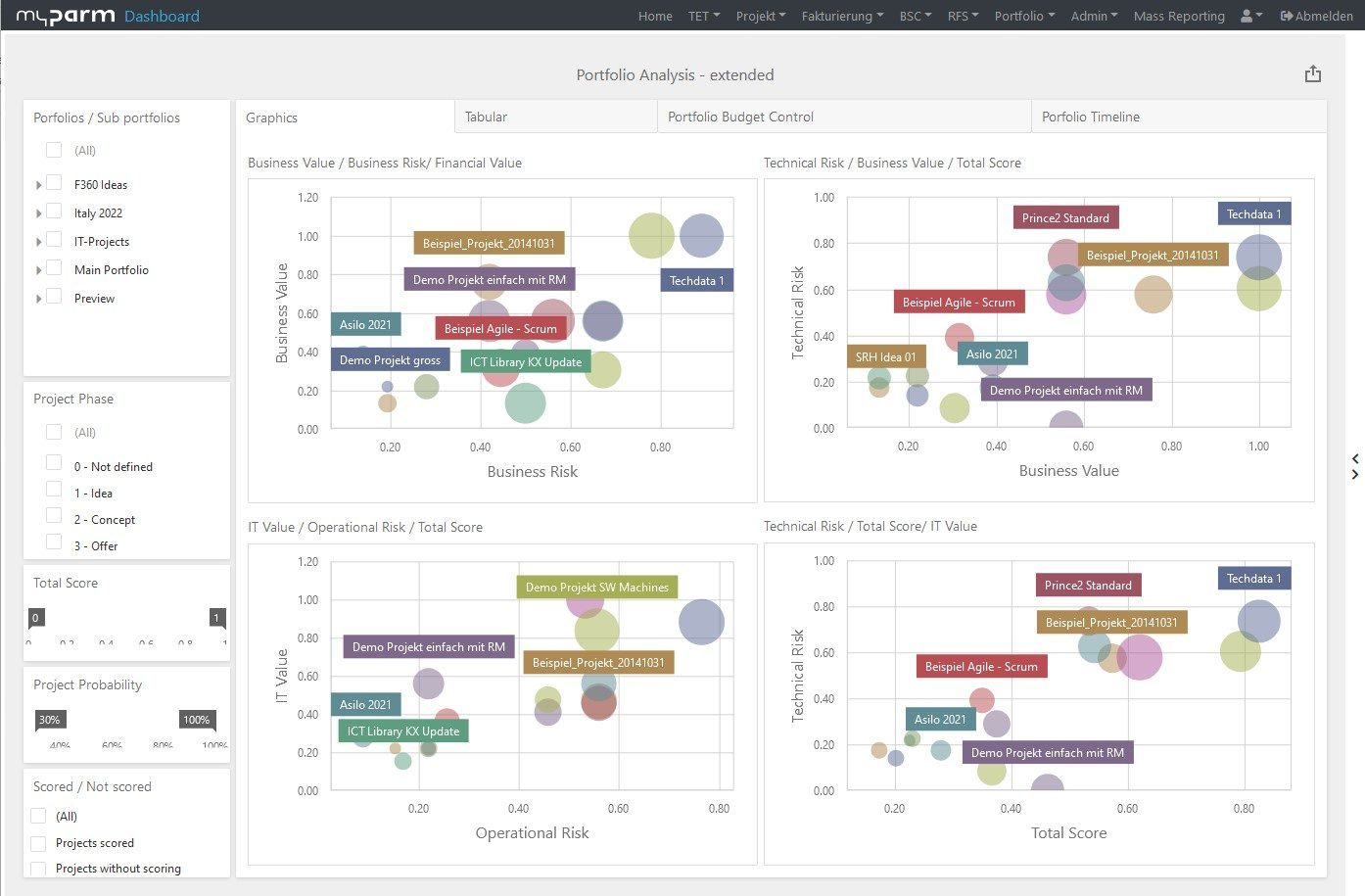
While a small project portfolio is still easily manageable, it quickly becomes confusing when there are numerous ideas and projects. However, good project management software also includes the possibility to control and monitor project portfolios. In this way, you can link the corporate strategy with the daily tasks, keep track of your tasks and projects at all times and evaluate projects or entire portfolios according to the criteria you define. The myPARM project management software allows you to collect projects and ideas, add them to different portfolios, and evaluate them. In this way, you can prioritise the individual projects and select those that best fit your corporate strategy. Keep an eye on your portfolios in the software at all times, create projects directly in the same system, and manage your resources there.
Learn more about the project and portfolio management software myPARM:
Would you like to get to know myPARM in a demo presentation? Then make an appointment with us right away!