Critical path
Critical Path in brief

In project management, a critical path is the longest chain of interdependent tasks for which a delay is should not occur. If tasks on this path are delayed, the completion of the entire project will be delayed. As a result, the critical path also determines the minimum duration of a project. The Critical Path Method (CPM) is used to highlight bottlenecks in the project and thus helps to identify possible delays in the project from the beginning so that measures can be taken against them. It also helps when the duration of a project needs to be shortened, as this should be addressed at the critical path.
Once a critical path has been identified, however, it does not always have to remain the same. If circumstances change, for example because more resources have been allocated to a task and it can therefore be completed in a shorter time, the critical path can shift to other tasks.
>>A critical path is the longest chain of interdependent tasks for which a delay is should not occur.<<
This is how the Critical Path Method works
1. list activities
As a basis for determining the critical path, you first need a list of all tasks that occur during the project. You can use a work breakdown structure, for example, to collect all activities and tasks.
2 Determine dependencies
Using the list of activities, you can then determine tasks that are dependent on each other. These are the tasks that must be completed before the next one can be started. This will also help to identify which tasks can be completed in parallel.
The following questions can help you to identify dependencies:
- Which tasks must be completed before the next task can be started?
- Which tasks must be completed at the same time?
- Which tasks should follow a particular task immediately?
Now transfer the activities and their dependencies into a network plan. This way you can see the chronological sequence of the activities and their dependencies at a glance. You can also add other time-bound components to the diagram, e.g. milestones that have to be reached by a specific date.
3. estimate task duration
Next, you should estimate the duration for each activity. There are several ways to do this.
- Estimation based on previous projects
- Informed forecasts based on your experience
- Estimation based on industry standards
4. Identify the critical path
The sequence of activities with the longest total duration is the critical path of your project. To identify it you can look at your network diagram and pick out the longest path. Alternatively, you can use forward or backward scheduling to identify the earliest and latest start and end points of a task, and thus also the associated start and end times of the project.
Ideally, this will provide you with a single critical path for your project. However, it is also possible that you get several critical paths. The more critical paths there are, the higher the probability that there will be changes to the schedule in the course of your project.
5. react
Once you have identified the critical path of a project, you can react to it. You can, for example, determine the earliest and latest start and end points of a project that are still within the project’s time schedule. This way you will know when the project should start at the latest in order to be finished on time. You can also see which activities are critical and which have buffer time. The latter are the activities that can be delayed without jeopardising the deadline of a project.
If the critical path is shorter than the planned project duration, you have a buffer for possible delays. However, you should still monitor the critical path while the project is being carried out in order to be able to react to delays in the process. As the duration of the tasks is only an estimation, the time actually needed for a task may differ from your planning. During the implementation of the project, you can use this information to assess how well you are on schedule and when the project can be completed.
If there are delays that would postpone the end of the project, you can try to reduce the duration of the critical path. There are several methods for this as well:
- Fast Tracking: examine the critical path to see if individual tasks or subtasks can possibly be carried out in parallel. This saves time during execution.
- Crashing: Allocate more resources to individual activities to speed up their execution.
For all changes, however, please ensure that the project scope is not exceeded and that all stakeholders are informed of the changes.
Advantages
- enables realistic time planning for projects
- improves resource management through better prioritisation of tasks
- helps to avoid bottlenecks and highlights risks
- shows the minimum duration of a project
- helps to react to delays of individual tasks
Disadvantages
- the critical path does not take into account the availability of the necessary resources of a project, which in turn can also lead to bottlenecks and delays in the project
Experts’ recommendation
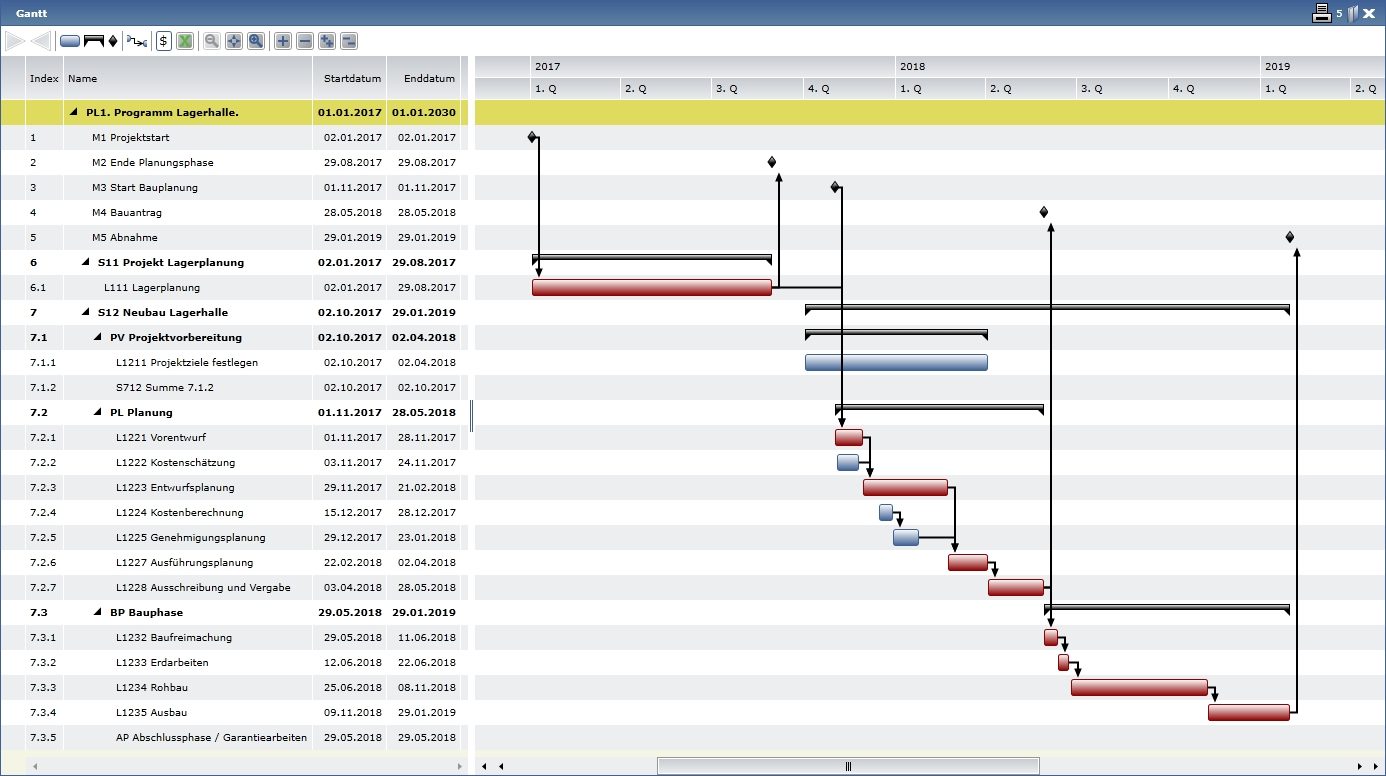
Combine the critical path with a Gantt chart to have an overview of the progress of the project activities on a time scale at any time while also integrating the resources of a project. In this way, you can best ensure that your project is proceeding according to plan.
Conclusion
The Critical Path Method is a useful aid to better plan and react in project management. However, in large projects with many activities, it is very difficult to identify and monitor the critical path alone. Modern project management software can help by visualising your project in a Gantt chart. This allows you to define all the characteristics of an activity, such as the earliest and latest start time, the earliest and latest end time, a buffer and the duration. In this way, the critical path can be calculated and visualised in a software-supported and automated way.
Use of CPM at Parm AG
The project management software myPARM allows you to display projects in a Gantt chart. The critical path is automatically marked so that you can keep an eye on it at all times.
More about the project management software myPARM:
Would you like to get to know myPARM in a demo presentation? Then make an appointment with us right away!